Industrial Laminators Overview: Explore Key Facts, Processes, and Essential Knowledge
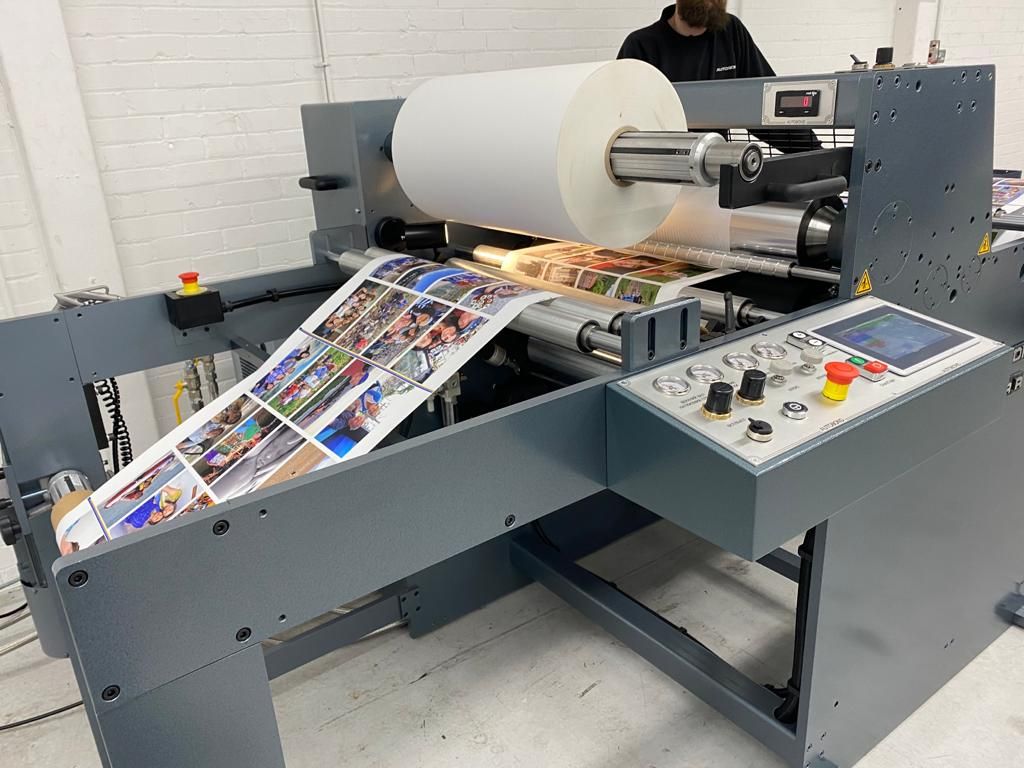
Industrial laminators are vital machines used in manufacturing and packaging industries to apply a protective layer over various materials such as paper, plastic, metal foil, or textiles. This process enhances durability, resistance to moisture, and visual appearance. From flexible packaging to automotive interiors, lamination technology plays an integral role in ensuring product quality and longevity.
Lamination is not limited to one industry. It extends across printing, electronics, construction, and renewable energy sectors. The continuous innovation in film materials and machinery design makes industrial laminators indispensable for modern production environments focused on quality, sustainability, and precision.

Understanding the Context
Industrial lamination technology evolved as industries began demanding materials that could withstand wear, heat, and environmental exposure. The process involves bonding two or more layers of material under pressure and temperature using adhesives or heat-activated films.
There are several main types of laminators:
-
Thermal laminators, which use heat to activate adhesive layers.
-
Cold laminators, which rely on pressure-sensitive adhesives.
-
Liquid laminators, used for coating flexible materials like banners or textiles.
-
Vacuum laminators, applied in electronics manufacturing, such as solar panels and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Industrial laminators are designed for continuous, high-volume production. They ensure consistent surface finishing, scratch resistance, and improved material integrity. In packaging, lamination prevents oxygen or moisture ingress, extending the shelf life of products.
Modern systems include advanced temperature control, digital monitoring, and energy-efficient components. These features improve accuracy and reduce waste, aligning with sustainability initiatives adopted by global manufacturers.
Why Industrial Laminators Matter Today
The importance of industrial laminators lies in their contribution to manufacturing efficiency, product protection, and design innovation. They help industries produce safer, more durable, and environmentally friendly materials.
Key reasons why industrial laminators matter include:
-
Enhanced Product Durability: Lamination adds protective layers that guard against water, dust, and UV exposure.
-
Sustainability and Recycling Goals: Eco-friendly films and adhesives reduce environmental impact.
-
Improved Aesthetic Appeal: Gloss, matte, or texture finishes elevate product presentation.
-
Growth in Flexible Packaging: The global demand for flexible packaging continues to increase, with laminators playing a central role.
-
Support for Electronics Manufacturing: Lamination is used to encapsulate delicate components, improving insulation and performance.
According to a 2024 market report, the global industrial laminating machine market has seen steady growth due to increasing adoption in food packaging, solar energy panels, and printed electronics. The trend toward recyclable films and solvent-free adhesives has also accelerated.
Recent Updates and Trends (2024–2025)
In the past year, several developments have shaped the industrial lamination sector. These updates reflect changing technologies, material science progress, and global manufacturing demands.
1. Automation and Smart Lamination Systems (2024–2025):
Manufacturers have begun integrating IoT-based sensors and AI-driven quality controls into laminators. These systems optimize temperature, pressure, and adhesive use in real time, reducing human error.
2. Eco-Friendly Lamination Materials (Late 2024):
With growing environmental regulations, many industries are transitioning to biodegradable or compostable laminating films. In 2024, several packaging companies introduced bio-based polymers compatible with existing laminating machinery.
3. Energy-Efficient Laminators:
New models introduced in early 2025 feature energy recovery mechanisms, reducing power consumption by up to 20%. This aligns with international carbon-reduction targets.
4. Digital Lamination Integration:
Hybrid machines now combine digital printing and lamination in a single line, streamlining operations for packaging and graphic industries.
5. Regional Growth:
Countries such as India, Vietnam, and Indonesia have seen significant growth in lamination-based manufacturing, supported by government initiatives encouraging industrial automation and green manufacturing.
Regulations, Standards, and Policies
Industrial laminators and the materials they use are subject to several global and national regulations. Compliance ensures safety, sustainability, and product quality.
Environmental and Safety Standards:
-
ISO 14001 and ISO 9001 certifications promote eco-friendly and quality-controlled manufacturing.
-
REACH and RoHS regulations in the European Union restrict the use of hazardous chemicals in lamination adhesives and coatings.
-
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) policies encourage the use of low-VOC (volatile organic compound) adhesives.
Packaging and Food Contact Regulations:
-
Lamination films used in food packaging must comply with FDA 21 CFR standards in the United States or EU Regulation 10/2011 for plastic materials in Europe.
-
In India, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) mandates testing for material migration and safety in laminated food-grade packaging.
Sustainability Programs:
Governments and international organizations are promoting recycling technologies and bio-based films. Programs under the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and OECD encourage green lamination practices and waste reduction.
These policies ensure that industrial lamination processes evolve responsibly while supporting innovation and compliance with environmental goals.
Tools and Resources
Professionals working with industrial laminators can benefit from several online tools, technical platforms, and educational resources. These resources help in process optimization, material selection, and environmental compliance.
Online Tools and Calculators:
-
Film Thickness Calculator: Estimates total lamination thickness based on film and adhesive layers.
-
Adhesive Coverage Estimator: Calculates adhesive usage per square meter for cost and efficiency analysis.
-
Energy Efficiency Analyzer: Tracks power consumption and identifies savings opportunities in lamination lines.
Websites and Databases:
-
ASTM International: Standards and testing procedures for laminated materials.
-
Packaging Europe and Plastics Today: Industry news, innovations, and sustainability updates.
-
ScienceDirect: Research papers on adhesive formulations and polymer science related to lamination.
-
ISO.org: Details on compliance and certification requirements.
Learning and Knowledge Platforms:
-
Coursera & EdX: Courses on industrial manufacturing, material engineering, and sustainability.
-
YouTube Engineering Channels: Practical tutorials on laminator maintenance and process calibration.
-
ResearchGate: Access to case studies and academic discussions on lamination efficiency and innovations.
These resources support continuous learning and help professionals maintain awareness of technological and regulatory developments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main purpose of industrial lamination?
Industrial lamination enhances material strength, durability, and visual appearance by bonding multiple layers under heat or pressure. It protects against damage, moisture, and contamination.
2. Which industries commonly use industrial laminators?
Laminators are widely used in packaging, printing, construction, automotive, textile, and electronics industries, particularly for making flexible packaging, labels, panels, and coated fabrics.
3. How has technology changed industrial lamination in recent years?
Recent innovations include automation, energy-efficient heating systems, eco-friendly adhesives, and real-time digital monitoring. These updates improve quality control and reduce waste.
4. Are there environmental concerns related to lamination?
Yes, traditional lamination can generate plastic waste and use solvent-based adhesives. However, newer technologies now use recyclable films and water-based adhesives to minimize impact.
5. What safety measures are important in lamination plants?
Operators must follow temperature and pressure guidelines, maintain proper ventilation, and use protective gear. Regular maintenance and quality checks ensure equipment safety and efficiency.
Conclusion
Industrial laminators play a central role in modern manufacturing, enhancing both product performance and sustainability. As industries move toward greener materials and smarter automation, lamination continues to evolve into a more efficient, controlled, and environmentally responsible process.
Understanding the materials, technologies, and regulations surrounding industrial lamination helps manufacturers achieve consistency, safety, and innovation in production. With the ongoing focus on eco-friendly solutions and digital integration, the future of industrial laminators promises smarter systems, minimal waste, and expanded industrial applications across global markets.