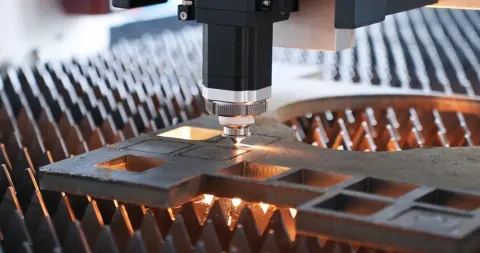
Discover How Fibre Laser Machines Deliver Faster and Cleaner Cutting
Fibre laser machines are industrial tools used to cut, engrave, or mark materials using a high-intensity laser beam generated through optical fiber. Unlike older laser systems, fibre lasers use solid-state technology, where the laser light is amplified inside a fiber optic cable rather than through gas or crystal-based systems.
This technology exists to meet the growing demand for precision, speed, and efficiency in manufacturing. As industries began working with thinner materials, complex shapes, and tighter tolerances, traditional cutting methods such as mechanical cutting or older laser systems showed limitations. Issues like excessive heat, rough edges, slower processing, and higher maintenance costs created a need for a more efficient solution.
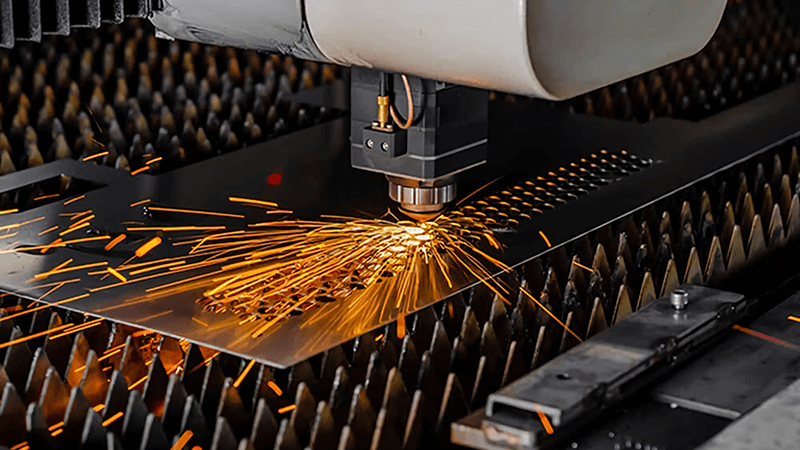

Fibre laser machines were developed to address these challenges. They allow manufacturers to cut metals and other materials with high accuracy, minimal waste, and cleaner edges. Today, they are widely used across industries that require reliable, repeatable, and precise cutting processes.
Importance – Why Fibre Laser Cutting Matters Today
Fibre laser machines are important because modern manufacturing relies on speed, consistency, and quality.
Supports Faster Production
High cutting speeds reduce processing time.
Delivers Cleaner Cutting Edges
Minimal burrs and smoother finishes reduce post-processing.
Improves Material Efficiency
Precise cutting lowers scrap and waste.
Reduces Operational Downtime
Fewer moving parts mean lower maintenance needs.
Supports Automation and Digital Manufacturing
Easily integrates with CNC and automated systems.
Who Uses Fibre Laser Machines
This technology is widely used by:
-
Metal fabrication workshops
-
Automotive component manufacturers
-
Electronics and electrical industries
-
Construction and infrastructure suppliers
-
Aerospace and engineering firms
-
Small and medium manufacturing units
Problems Fibre Laser Machines Help Solve
-
Slow cutting speeds
-
Inconsistent cut quality
-
Excessive heat distortion
-
High material waste
-
Frequent machine maintenance
As industries focus on efficiency and sustainability, fibre laser cutting has become a preferred solution.
How Fibre Laser Machines Work
Understanding the basic working principle helps explain their advantages.
Core Working Process
-
Laser light is generated by a diode
-
Light is amplified through an optical fiber
-
The focused beam melts or vaporizes material
-
Assist gas removes molten material from the cut
Key Characteristics
-
High energy density
-
Stable beam quality
-
Precise focus control
Basic Process Overview
| Step | Function |
|---|---|
| Laser generation | Creates high-energy beam |
| Fiber transmission | Maintains beam quality |
| Focusing lens | Concentrates energy |
| Cutting head | Directs laser path |
| Assist gas | Clears cut area |
This controlled process results in clean and accurate cuts.
Recent Updates – Fibre Laser Cutting Trends (2024–2025)
Over the past year, fibre laser technology has continued to evolve.
Higher Power Fibre Lasers (2024)
Manufacturers introduced higher wattage machines for thicker materials.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
New systems focused on reduced power consumption.
Integration With Smart Manufacturing
Machines increasingly connected with monitoring and analytics software.
Improved Cutting Heads
Enhanced autofocus and motion control improved consistency.
Growth in Small Workshop Adoption
Compact fibre laser machines became more accessible to smaller units.
These updates reflect a trend toward smarter, faster, and more efficient cutting solutions.
Materials Commonly Cut Using Fibre Laser Machines
Fibre laser machines are versatile and support a wide range of materials.
Commonly Processed Materials
-
Mild steel
-
Stainless steel
-
Aluminum
-
Brass
-
Copper
-
Thin alloys
Material Compatibility Overview
| Material | Cutting Performance |
|---|---|
| Mild steel | Very efficient |
| Stainless steel | Clean and precise |
| Aluminum | Fast with proper settings |
| Copper | Requires higher power |
| Brass | Controlled cutting |
This versatility makes fibre lasers suitable for diverse applications.
Importance of Cleaner Cutting in Manufacturing
Cleaner cutting improves both product quality and workflow efficiency.
Benefits of Cleaner Edges
-
Reduced need for secondary finishing
-
Better part fitting and assembly
-
Improved surface appearance
-
Lower production time
Comparison of Cut Quality
| Aspect | Traditional Cutting | Fibre Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Edge finish | Rougher | Smooth |
| Heat distortion | Higher | Minimal |
| Accuracy | Variable | High |
| Waste | Higher | Lower |
Cleaner cuts contribute to overall manufacturing consistency.
Laws or Policies – Regulations Affecting Fibre Laser Operations
Fibre laser machines operate within industrial safety and environmental regulations.
Workplace Safety Regulations
Require protective enclosures, eyewear, and training.
Laser Classification Standards
Define laser power categories and usage guidelines.
Environmental Compliance Rules
Control emissions, fumes, and waste disposal.
Electrical and Machinery Safety Standards
Ensure safe installation and operation.
Occupational Health Policies
Protect workers from exposure risks.
These policies promote safe and responsible use of laser technology.
Tools and Resources – Helpful Support for Fibre Laser Cutting
Several tools and resources support efficient use of fibre laser machines.
Useful Tools and Resources
| Tool / Resource | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CNC Control Software | Machine programming |
| Laser Parameter Calculators | Optimize cutting settings |
| Maintenance Schedules | Reduce downtime |
| Safety Training Materials | Operator awareness |
| CAD/CAM Software | Design and nesting |
| Material Databases | Cutting reference data |
| Energy Monitoring Tools | Efficiency tracking |
These tools help maintain consistent performance and safety.
Operational Benefits Beyond Speed
Fibre laser machines provide advantages beyond faster cutting.
Low Maintenance Requirements
Solid-state design reduces component wear.
Compact Machine Footprint
Saves floor space compared to older systems.
High Repeatability
Ensures consistent results across batches.
Automation Friendly
Supports robotic loading and unloading.
Operational Benefit Summary
| Area | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Maintenance | Reduced |
| Space | Efficient |
| Accuracy | High |
| Integration | Easy |
These benefits support long-term operational stability.
FAQs – Clear and Factual Answers
What is a fibre laser machine?
A fibre laser machine uses a fiber optic system to generate and deliver a high-energy laser beam for cutting materials.
Why are fibre lasers considered faster?
They offer higher energy efficiency and faster beam movement, which increases cutting speed.
Are fibre laser cuts cleaner than traditional methods?
Yes. They produce smoother edges with less heat impact.
What industries commonly use fibre laser cutting?
Metal fabrication, automotive, electronics, and engineering industries widely use it.
Do fibre laser machines require special safety measures?
Yes. Proper shielding, training, and protective equipment are required.
Final Thoughts
Fibre laser machines have become an important part of modern manufacturing by delivering faster and cleaner cutting results. Their ability to produce precise cuts with minimal waste supports efficiency, quality, and sustainability. Recent advancements in power, automation, and energy efficiency have further expanded their applications across industries. Guided by safety regulations and supported by digital tools, fibre laser cutting continues to offer a reliable and adaptable solution for today’s production needs.