Learn the Basics: How Wire Drawing Machines Improve Wire Quality
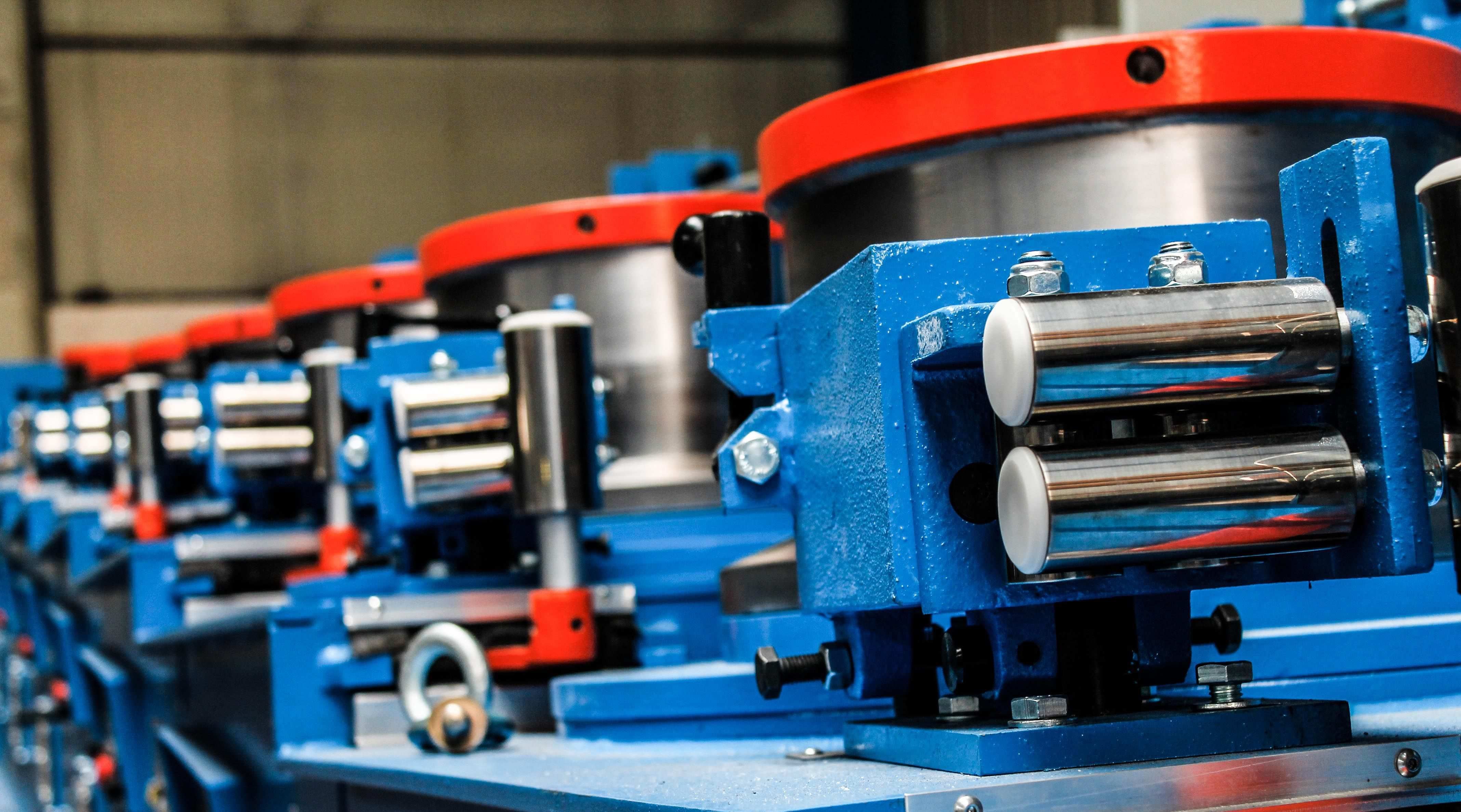
Wire drawing machines are industrial systems used to reduce the diameter of metal wires while improving their surface finish, strength, and uniformity. The process works by pulling the wire through a series of dies, gradually making it thinner and more refined. This technology exists because industries require wires with specific sizes, smoothness, and mechanical properties for electrical, construction, automotive, and manufacturing use.
Wire drawing has been a vital part of metal processing for decades, with machines evolving to deliver higher accuracy, better speed, and improved energy efficiency. From basic mechanical systems to advanced automated models, these machines are essential in producing the consistent wire quality required for modern applications.
Importance
Wire drawing machines play a major role in manufacturing materials used in daily life. As industries demand more precise and higher-quality wire, the importance of reliable drawing technology continues to grow.
Why This Topic Matters Today
-
Increasing demand for fine-quality wire: Industries such as electronics, construction, and automotive require wires with uniform size and strong mechanical properties.
-
Higher expectations of consistency: Manufacturers often need wire that meets strict standards for conductivity, surface smoothness, and tensile strength.
-
Improved production efficiency: Modern drawing machines help companies produce more wire in less time while maintaining quality.
-
Growing use of automated systems: Automation reduces manual errors and enables precise control over drawing speed and pressure.
Who It Affects
-
Wire manufacturing companies
-
Electrical cable producers
-
Automotive component manufacturers
-
Steel and metal processing industries
-
Small and medium enterprises involved in wire-based products
Problems Wire Drawing Machines Help Solve
-
Uneven wire diameters
-
Rough or inconsistent surfaces
-
Low tensile strength
-
High production costs caused by manual processing
-
Inconsistent material properties in large volumes
Wire drawing machines improve quality and reliability, enabling industries to meet product requirements more efficiently.
Recent Updates
Recent developments in wire drawing technology reflect the increasing focus on automation, precision, and sustainability.
Key Industry Trends (2024–2025)
-
Adoption of smart monitoring systems: Machines now include sensors that track die wear, lubrication levels, and wire tension.
-
Energy-efficient models released in 2024: Several manufacturers introduced energy-saving motors and optimized cooling systems to reduce operational costs.
-
Greater interest in multi-wire drawing: Multi-line machines allow producers to run several wires simultaneously, improving output without expanding floor space.
-
New coating and lubrication technologies: Modern lubricants reduce friction, lower die wear, and help maintain wire smoothness.
-
Enhanced safety features: Updated designs include better guarding systems, emergency controls, and operator-friendly panels.
Simple Comparison Table: Types of Wire Drawing Machines
| Machine Type | Key Features | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Single Block | One capstan, simple operation | Small-scale wire reduction |
| Multi-Block | Multiple capstans, higher speed | Medium to large production |
| Straight-Line | Minimal wire torsion, smooth operation | High-quality wire products |
| Horizontal Drawing | Ideal for thick and heavy wires | Steel and industrial applications |
| Fine Wire Drawing | Precision dies, low tension | Electronics and thin wire manufacturing |
These updates show the industry’s shift toward better performance, safety, and cost efficiency.
Laws or Policies
Wire drawing machines must adhere to several industrial and safety regulations depending on the country of operation.
Key Regulations That Influence Wire Drawing Operations
-
Industrial safety guidelines: Many regions require proper machine guarding, operator training, and emergency stop features.
-
Environmental policies: Regulations may cover waste management, lubricant disposal, and energy efficiency.
-
Quality standards: Wire products often follow national or international standards related to tensile strength, diameter tolerance, and surface finish.
-
Electrical equipment rules: Machines must comply with electrical safety regulations to ensure safe installation and operation.
-
Manufacturing compliance: Some countries require factory inspections or certifications for large-scale wire production facilities.
These policies help maintain safe working conditions and ensure reliable product quality.
Tools and Resources
Several tools and resources support wire drawing operations, machine selection, and quality control.
Useful Tools and Resources
-
Wire Diameter Calculators – Estimate reduction sizes and drawing ratios
-
Material Hardness Charts – Identify suitable drawing speeds for different metals
-
Lubrication Guides – Provide recommendations for friction reduction
-
Maintenance Planning Templates – Help track die changes, lubrication schedules, and machine servicing
-
Industry Standards Websites – Provide specifications for wire manufacturing
-
Monitoring Apps – Used for automated machine data tracking
-
Training Videos and Manuals – Help operators understand setup and safety procedures
Wire Drawing Reduction Table Example
| Stage | Input Diameter | Output Diameter | Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.0 mm | 5.5 mm | 15% |
| 2 | 5.5 mm | 5.0 mm | 18% |
| 3 | 5.0 mm | 4.5 mm | 19% |
Such tables help planners design accurate multi-stage drawing processes.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of wire drawing?
The main purpose is to reduce the diameter of metal wire while improving its surface quality and mechanical strength.
2. Which materials can be processed using wire drawing machines?
Common materials include copper, aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass, and various alloys.
3. How often do drawing dies need to be replaced?
The replacement frequency depends on production volume, lubricant quality, and wire hardness. Some dies last weeks, while others may need earlier servicing.
4. Is lubrication important in wire drawing?
Yes. Proper lubrication reduces friction, improves wire surface quality, and helps extend die life.
5. Can wire drawing machines be automated?
Many modern machines include automated controls, monitoring sensors, and electronic speed adjustment systems.
Final Thoughts
Wire drawing machines play a central role in producing high-quality metal wire for industries around the world. By refining diameter, increasing strength, and improving surface consistency, these machines support a wide range of applications from electrical cables to construction materials. Understanding the different machine types, recent advancements, regulatory requirements, and available tools helps manufacturers choose suitable solutions and maintain efficient production. As the demand for refined wire continues to grow, wire drawing technology will remain a crucial part of metal processing operations.






