Traditional cheese production relied heavily on manual handling, open vats, and human judgment. While craftsmanship remains valuable, modern food production requires predictable quality, traceability, and regulatory alignment. Automated cheese production equipment helps standardize temperature control, agitation, cutting precision, moisture management, and sanitation cycles.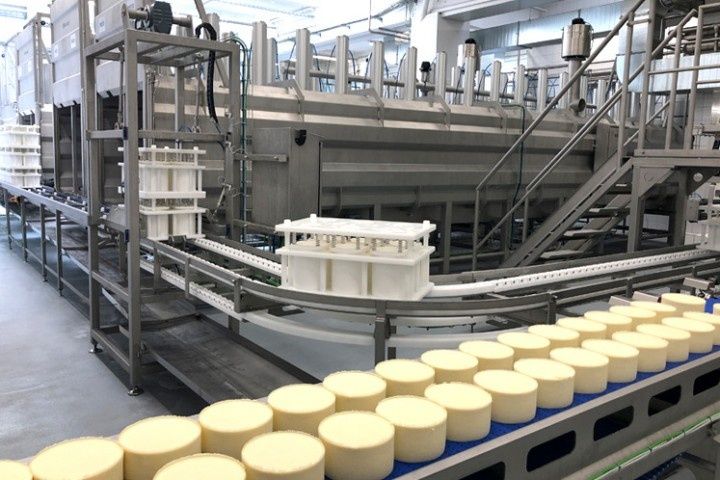
Today, cheese manufacturing integrates stainless steel dairy equipment, programmable logic controllers (PLC), and clean-in-place (CIP) sanitation systems. This approach supports controlled processing, minimizes contamination risk, and enables producers to handle increasing volume demands while maintaining food safety expectations.
Why Cheese Making Machines Matter Today
Cheese consumption continues to expand across households, hospitality supply chains, packaged food manufacturing, and export-oriented dairy markets. As product diversity increases — from fresh cheeses to aged varieties consistency and hygiene become essential. Cheese making machines address these operational needs while supporting sustainability and traceability goals.
Key reasons these machines matter include:
-
Standardized production quality through precise temperature, mixing, and timing control
-
Food safety assurance supported by sealed systems and automated cleaning protocols
-
Production scalability enabling higher throughput without manual overload
-
Reduced variability in texture, moisture content, and yield stability
-
Data-driven process optimization using sensor feedback and PLC control systems
-
Labor efficiency through automation of repetitive processing steps
Industries influenced by cheese making equipment include dairy processors, food packaging facilities, cold-chain logistics planners, agricultural cooperatives, and food quality laboratories. Engineers, quality analysts, and regulatory auditors also depend on accurate machine data to verify compliance.
Cheese making machines solve practical challenges such as contamination risk, inconsistent batch outcomes, manual handling limitations, and complex sanitation management.
Recent Developments and Industry Direction
Over the past year, several technology shifts have influenced industrial cheese production environments. While the fundamentals remain stable, digitalization and sustainability initiatives continue to shape equipment development.
Notable developments observed during 2024–2025 include:
-
Increased adoption of automated cheese processing equipment integrated with cloud dashboards for batch tracking and performance analytics
-
Expanded use of energy-efficient heat recovery systems in pasteurization modules to improve thermal efficiency
-
Growth of smart sensor integration for pH monitoring, curd firmness analysis, and whey separation accuracy
-
Broader deployment of CIP optimization algorithms that reduce water usage while maintaining sanitation reliability
-
Enhanced traceability features aligned with digital food safety documentation standards
-
Rising interest in modular processing lines that allow flexible product variation without major reconfiguration
These updates demonstrate a movement toward intelligent food processing automation, predictive maintenance, and environmentally conscious production strategies.
Table: Technology Evolution in Cheese Production Equipment
| Area | Earlier Approach | Current Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Manual thermostat adjustment | Digital PID controllers |
| Cleaning | Manual disassembly | Automated CIP systems |
| Data Logging | Paper batch logs | Digital production records |
| Process Monitoring | Visual inspection | Sensor-driven analytics |
| Flexibility | Fixed configuration | Modular production lines |
Regulatory and Policy Environment
Cheese production machinery operates within strict food safety and industrial compliance frameworks. Regulations vary by country but share common objectives: consumer safety, traceability, hygienic processing, and equipment reliability.
Typical regulatory considerations include:
-
Food safety standards governing material compatibility, sanitation procedures, and microbial control
-
Dairy processing regulations covering milk handling, pasteurization validation, and storage conditions
-
Equipment safety norms related to electrical protection, pressure systems, and mechanical guarding
-
Environmental compliance linked to wastewater discharge, chemical handling, and energy efficiency
-
Traceability documentation requiring batch identification and process logging
In many regions, dairy facilities align with national food safety authorities and international quality frameworks such as HACCP principles and ISO food safety management systems. Machine documentation, calibration records, and sanitation validation logs support regulatory audits and operational transparency.
Policy alignment ensures that cheese making machines function safely, protect public health, and support sustainable manufacturing practices.
Tools, Digital Resources, and Knowledge Aids
Operators and engineers rely on a variety of digital and technical tools to maintain performance, safety, and efficiency.
Helpful resources include:
-
PLC configuration platforms for controlling automated cheese production equipment
-
CIP validation checklists supporting sanitation verification
-
Production batch tracking software for traceability and reporting
-
Sensor calibration tools for pH, temperature, and flow measurement accuracy
-
Maintenance scheduling templates supporting predictive inspection planning
-
Process simulation tools for workflow optimization
-
Food safety documentation libraries providing regulatory guidance
-
Energy monitoring dashboards for thermal and electrical efficiency analysis
These resources strengthen operational consistency and knowledge sharing across dairy processing teams.
Process Flow and Operational Understanding
A typical cheese production line integrates multiple machines working in sequence. While configurations vary, the core workflow follows a structured path.
Common operational stages include:
-
Milk preparation and pasteurization
Temperature-controlled heating ensures microbial stability and consistent protein behavior. -
Curd formation and coagulation
Agitators and dosing systems regulate enzyme distribution and curd texture development. -
Cutting and whey separation
Automated knives and drainage modules manage moisture balance. -
Molding and pressing
Mechanical presses define shape, density, and internal structure. -
Cooling and stabilization
Controlled environments prepare products for aging or packaging stages.
Table: Key Machine Types and Functional Role
| Machine Category | Functional Purpose | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pasteurization Unit | Thermal treatment of milk | Microbial stability |
| Coagulation Vat | Curd formation control | Texture consistency |
| Curd Cutter | Particle sizing | Moisture regulation |
| Pressing Module | Shape and density formation | Structural stability |
| CIP System | Automated sanitation | Hygiene assurance |
Practical Insights and Operational Guidance
Efficient machine utilization depends on disciplined monitoring and routine evaluation rather than reactive correction.
Helpful practices include:
-
Establish baseline operating parameters for temperature, flow, and agitation
-
Validate sensor calibration periodically to avoid data drift
-
Monitor CIP cycle effectiveness through residue testing
-
Track batch consistency using digital logs rather than manual notes
-
Analyze energy consumption trends for optimization opportunities
-
Maintain spare component readiness for critical wear parts
-
Review vibration and motor load indicators to detect early mechanical stress
-
Align production scheduling with sanitation windows for smooth transitions
Well-structured documentation improves audit readiness and knowledge continuity across operational teams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are cheese making machines used for?
They automate and control milk processing steps such as heating, coagulation, cutting, pressing, and sanitation in structured dairy environments.
Are automated cheese processing systems suitable for multiple cheese varieties?
Yes. Modular configurations and programmable controls allow adjustments for temperature, timing, and agitation to support different product styles.
How does a CIP system support hygiene?
It circulates cleaning solutions through internal pipelines and tanks without dismantling equipment, ensuring consistent sanitation coverage.
What role does PLC automation play?
PLC systems coordinate sensors, motors, valves, and alarms to maintain stable processing conditions and generate operational data logs.
Why is stainless steel commonly used in dairy equipment?
Stainless steel resists corrosion, supports hygienic cleaning, and maintains structural durability in food-contact environments.
Conclusion
Cheese making machines play a foundational role in modern dairy processing. By integrating automation, digital monitoring, and hygienic engineering, these systems enable reliable transformation of milk into consistent cheese products. They support operational efficiency, regulatory alignment, traceability, and long-term asset stability.
As industrial cheese production continues to evolve, emphasis on smart sensors, energy efficiency, modular flexibility, and predictive maintenance will further strengthen production reliability. Understanding how these machines function from curd formation to sanitation automation helps stakeholders interpret performance data, maintain quality consistency, and support responsible manufacturing practices.
Cheese making machines represent a convergence of food science, mechanical engineering, and digital automation, forming a dependable foundation for structured dairy production in modern processing environments.