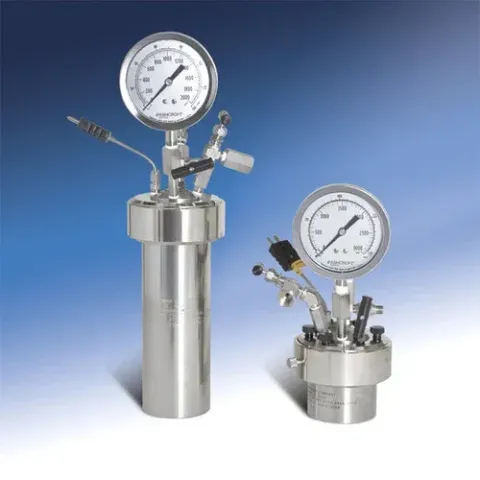
Discover How Pressure Reactors Improve Process Efficiency and Safety
Pressure reactors are specialized industrial vessels designed to carry out chemical reactions under controlled pressure and temperature conditions. They are commonly used in industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, polymers, fertilizers, food processing, and materials research. Unlike open or atmospheric reactors, pressure reactors allow reactions to occur in sealed environments where pressure, heat, and reaction rates can be precisely managed.
Historically, many chemical reactions were performed at atmospheric pressure. While suitable for basic processes, this approach limited reaction speed, yield, and control. Certain reactions require higher pressure to proceed efficiently or safely, especially when gases are involved or when reactions release heat rapidly. Operating such reactions without proper containment increased risks of leaks, runaway reactions, or product inconsistency.

Pressure reactors were developed to address these limitations. By enclosing reactions within strong, engineered vessels, manufacturers could safely handle higher pressures and temperatures. This allowed faster reactions, improved conversion rates, and better control over product quality. Over time, pressure reactors became essential tools for modern industrial processing where efficiency and safety must coexist.
Importance – Why Pressure Reactors Matter Today
Pressure reactors play a critical role in modern manufacturing and research by improving both operational efficiency and safety.
Improves Reaction Efficiency
Higher pressure often increases reaction rates, allowing processes to complete faster.
Enhances Product Yield and Consistency
Controlled conditions lead to uniform reactions and predictable product quality.
Supports Safer Chemical Processing
Sealed designs reduce exposure to hazardous substances and prevent uncontrolled releases.
Enables Complex and Advanced Reactions
Many modern chemical processes are only possible under elevated pressure.
Optimizes Energy and Resource Use
Efficient reactions reduce waste, reprocessing, and energy consumption.
Benefits Multiple Stakeholders
Pressure reactors support:
-
Chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturers
-
Research and development teams
-
Process engineers and safety officers
-
Regulatory and compliance teams
Solves Common Industrial Challenges
Well-designed pressure reactors help address:
-
Slow or incomplete reactions
-
Process instability and variability
-
Safety risks from volatile reactions
-
Excessive material waste
-
Difficulty scaling laboratory processes to production
As industries pursue higher productivity with lower risk, pressure reactors remain a key solution.
Recent Updates – Trends and Developments in 2024–2025
Pressure reactor technology has continued to evolve over the past year, driven by safety, efficiency, and sustainability goals.
Advanced Materials for Reactor Construction (2024)
New alloys and linings improved resistance to corrosion and high temperatures.
Digital Monitoring and Automation
Sensors and control systems enabled real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and reaction progress.
Improved Safety Interlocks and Fail-Safe Systems
Modern reactors included automated shutdown features to prevent unsafe conditions.
Scalable Reactor Designs
Manufacturers introduced modular reactor systems for easier scale-up from pilot to production.
Focus on Sustainable Processing
Pressure reactors were adapted to support greener chemistry and reduced solvent usage.
Enhanced Data Collection for Process Optimization
Operational data was increasingly analyzed to improve reaction efficiency and predict maintenance needs.
These developments reflect a strong focus on combining productivity with enhanced safety controls.
Laws or Policies – Regulations Affecting Pressure Reactor Use
Pressure reactors are subject to strict regulatory oversight due to the risks associated with high-pressure operations.
Pressure Vessel Safety Regulations
Design, manufacturing, and operation must meet national and international pressure vessel standards.
Industrial Safety and Occupational Health Laws
Operators must be protected from hazards such as high pressure, heat, and chemicals.
Environmental Protection Regulations
Controlled reactors help prevent emissions and accidental releases into the environment.
Process Safety Management Requirements
Many jurisdictions require documented risk assessments and safety procedures.
Inspection and Certification Policies
Pressure reactors must undergo periodic inspection and certification to remain operational.
Compliance with these regulations ensures safe operation and protects both workers and the surrounding environment.
Tools and Resources – Helpful Support for Pressure Reactor Operations
Several tools and resources support efficient and safe use of pressure reactors.
Useful Tools and Resources
| Tool / Resource | Purpose / Benefit |
|---|---|
| Pressure Reactors | Enable controlled high-pressure reactions |
| Pressure and Temperature Sensors | Monitor reaction conditions |
| Automated Control Systems | Maintain stability and consistency |
| Safety Relief Valves | Prevent overpressure situations |
| Data Logging Software | Track process performance |
| Material Compatibility Guides | Ensure safe reactor construction |
| Maintenance and Inspection Checklists | Support compliance |
| Process Simulation Software | Optimize reaction design |
These tools help maintain reliable, safe, and efficient reactor operations.
FAQs – Clear and Factual Answers
What is a pressure reactor?
A pressure reactor is a sealed vessel designed to carry out chemical reactions under controlled pressure and temperature.
Why are pressure reactors safer than open systems?
They contain reactions within engineered vessels, reducing exposure and controlling pressure release.
Do pressure reactors improve production efficiency?
Yes. Higher pressure often leads to faster reactions and better conversion rates.
Are pressure reactors used only in chemical plants?
No. They are also used in pharmaceuticals, food processing, materials research, and energy industries.
Do pressure reactors require regular inspections?
Yes. Regular inspection and certification are essential for safe operation.
Final Thoughts
Pressure reactors are essential tools for modern industrial processing, offering a balance between efficiency and safety. By enabling precise control over pressure and temperature, they allow reactions to proceed faster, more consistently, and with reduced risk. Recent advancements in materials, automation, and monitoring have further improved their reliability and usability. When operated within regulatory guidelines and supported by proper maintenance and training, pressure reactors contribute to safer workplaces, higher-quality products, and more efficient industrial operations across a wide range of sectors.