Chemical Dosing Systems Explained: A Complete Guide to Function, Design, and Operation Insights
Chemical dosing systems are essential components in many industrial and environmental processes. They are designed to automatically measure and deliver precise amounts of chemicals into water, wastewater, or other fluid streams. These systems ensure accurate chemical treatment, helping industries maintain quality, safety, and compliance standards.
At their core, chemical dosing systems consist of a storage tank, dosing pump, control unit, and monitoring instruments. Each part works together to ensure consistent delivery of chemicals like chlorine, acids, alkalis, or coagulants.
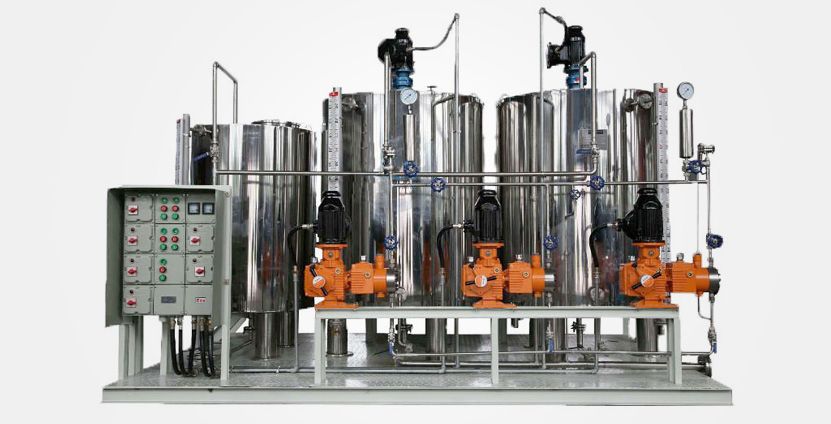

They are used across multiple sectors—such as water treatment, power generation, food processing, and pharmaceuticals—where controlled chemical addition is critical for processes like disinfection, pH correction, and corrosion prevention.
Why Chemical Dosing Systems Matter Today
Precise chemical dosing is vital for maintaining operational safety, environmental protection, and process efficiency. Inaccurate chemical addition can lead to system inefficiencies, contamination, or regulatory non-compliance.
Key areas where dosing systems make a difference:
-
Water and wastewater treatment: Ensures proper disinfection, prevents harmful bacterial growth, and controls chemical residues.
-
Industrial production: Maintains process balance and product consistency.
-
Power generation: Prevents corrosion in boilers and cooling systems by maintaining chemical equilibrium.
-
Agriculture and aquaculture: Delivers nutrients or disinfectants in controlled quantities to maintain ecosystem balance.
Accurate dosing reduces chemical waste, minimizes environmental risks, and lowers maintenance requirements. With growing global attention on sustainability and water conservation, modern chemical dosing technologies are becoming more intelligent and automated.
Recent Developments and Technological Trends
Over the past year, several advancements have shaped the field of chemical dosing systems, driven by digital transformation and sustainability efforts.
1. Smart Dosing Systems (2024–2025):
Recent developments have integrated Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for real-time monitoring and adaptive control. Smart dosing systems can automatically adjust chemical feed rates based on changing process conditions, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
2. Energy-Efficient Pumps:
New-generation diaphragm and peristaltic pumps consume less power while providing greater accuracy. These designs reduce operational costs and carbon footprints.
3. Green Chemical Formulations:
Manufacturers have started adopting eco-friendly chemical formulations that require precise dosing to minimize ecological impact.
4. Remote Operation and Cloud Analytics:
By late 2024, cloud-based monitoring platforms became more common in industrial facilities. They allow operators to track chemical usage, alarm notifications, and dosing performance from mobile devices.
5. Safety Standards and Automation:
Automated shut-off valves and leak detection sensors have become standard components, enhancing workplace safety and reducing manual intervention.
Trend Snapshot (2024–2025):
| Trend Area | Description | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|
| IoT Integration | Real-time monitoring and data-driven dosing | Higher efficiency |
| Eco Formulations | Sustainable chemical alternatives | Lower environmental footprint |
| Automation | AI-controlled dosing precision | Reduced human error |
| Cloud Monitoring | Centralized control and analytics | Better decision-making |
These innovations highlight how technology continues to transform traditional dosing systems into intelligent process control tools.
Regulatory Standards and Environmental Policies
Chemical dosing systems operate within a framework of international and national regulations designed to ensure environmental safety and public health.
In India, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) provide guidelines for water treatment, discharge quality, and chemical handling. Specific regulations include:
-
Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974: Governs water quality and pollution control, requiring precise dosing to meet discharge standards.
-
Environment (Protection) Act, 1986: Sets limits for chemical contaminants and mandates treatment system monitoring.
-
BIS IS 10500:2012: Defines drinking water standards, ensuring chemical dosing maintains safe levels for public consumption.
Globally, organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) set guidelines for chemical concentrations in treated water and industrial effluent.
Compliance with these regulations ensures that dosing systems contribute to sustainable and safe operations. Automated systems with data logging features also simplify documentation for audits and regulatory reporting.
Tools, Software, and Learning Resources
Modern dosing systems benefit from specialized tools and platforms that enhance efficiency, monitoring, and learning.
Technical Tools and Calculators:
-
Online Dosing Rate Calculator: Helps determine chemical feed rates based on concentration and flow rate.
-
pH and Chlorine Monitoring Apps: Used to check chemical balance in real time.
-
Flow Meter Selection Guide: Assists in choosing the right flow measurement tool for dosing accuracy.
Software and Monitoring Platforms:
-
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition): Commonly used in industries for integrated system monitoring and control.
-
PLC-Based Control Systems: Provide programmable logic for automatic dosing adjustments.
-
Cloud Analytics Dashboards: Platforms like Siemens MindSphere and ABB Ability enable data visualization, maintenance alerts, and system optimization.
Educational Resources:
-
Indian Water Works Association (IWWA) – Offers training modules on water treatment technologies.
-
World Health Organization (WHO) – Publishes international standards on chemical dosing in water treatment.
-
ResearchGate and ScienceDirect – Provide research papers on emerging dosing technologies.
Example of Dosing Efficiency Comparison:
| Dosing Type | Typical Accuracy (%) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Dosing | 70–80 | Small-scale processes |
| Semi-Automatic | 85–90 | Mid-range operations |
| Fully Automated | 95–99 | Industrial and municipal systems |
These resources help engineers, students, and professionals understand system operation, select components, and maintain safe chemical balance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary function of a chemical dosing system?
A chemical dosing system is designed to accurately add specific quantities of chemicals into a process stream to achieve a desired reaction, such as disinfection, pH adjustment, or corrosion control.
2. How does an automatic dosing system differ from a manual one?
Automatic systems use sensors, controllers, and pumps to maintain chemical levels based on real-time data. Manual systems require operator intervention and are less consistent.
3. What types of pumps are commonly used in dosing systems?
Diaphragm, peristaltic, and solenoid-driven pumps are commonly used, each offering varying levels of accuracy and pressure handling for different industrial applications.
4. How often should dosing systems be calibrated?
Calibration should typically be performed every 3–6 months, depending on usage intensity and the type of chemicals being handled, to maintain dosing precision.
5. Are chemical dosing systems environmentally friendly?
When properly designed and operated, they minimize chemical waste and environmental discharge, supporting sustainable industrial operations.
Conclusion
Chemical dosing systems play an indispensable role in modern water treatment, manufacturing, and environmental management. Their ability to deliver precise chemical quantities supports quality control, safety, and sustainability goals across multiple industries.
As technology continues to advance, the shift toward automated, data-driven dosing systems marks a significant step in improving operational efficiency and environmental protection. With regulatory frameworks evolving and smart technologies emerging, understanding the function, design, and operation of chemical dosing systems is more relevant than ever.
For students, engineers, and facility managers alike, a foundational knowledge of these systems helps ensure that industrial and environmental processes remain efficient, compliant, and sustainable for the future.