The Complete Guide to Industrial Heat Exchangers: Facts, Functions, and Knowledge
Industrial heat exchangers are essential devices used to transfer heat between two or more fluids—such as liquids, gases, or a combination of both—without mixing them. They exist because industries require efficient ways to manage heat during various processes, from power generation and chemical production to food processing and HVAC systems.
These systems play a key role in optimizing energy use by recovering heat from one process and reusing it elsewhere, reducing waste and improving sustainability. The concept of heat exchange has existed for over a century, evolving with technological advances to improve efficiency, durability, and environmental performance.
In essence, industrial heat exchangers enable temperature control in systems where direct contact between fluids is not possible or desired. This control ensures safe, continuous, and cost-efficient operations across multiple sectors.
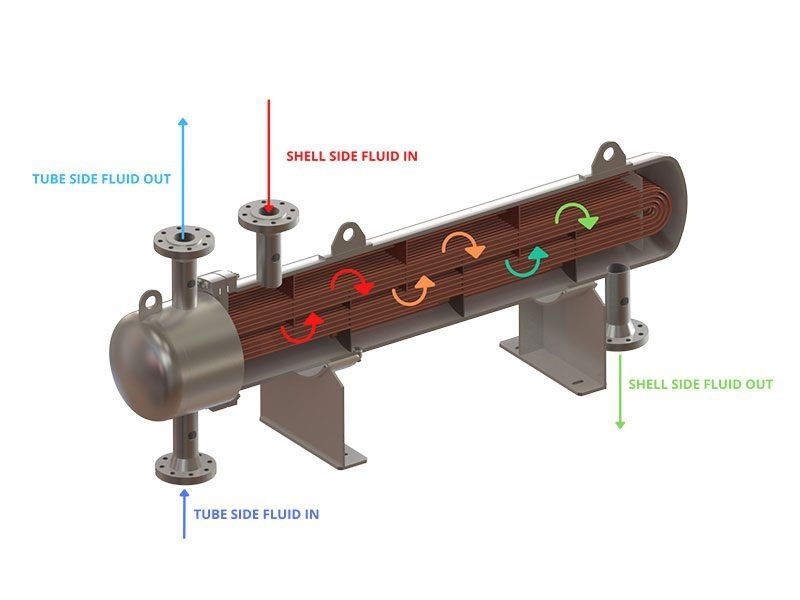
Importance
Industrial heat exchangers are vital for modern industry because they directly influence efficiency, safety, and environmental impact. Their importance can be understood through the following factors:
-
Energy efficiency: By recovering and reusing heat, they reduce the need for additional energy sources, leading to lower fuel consumption.
-
Process stability: Maintaining consistent temperatures prevents overheating or undercooling, ensuring stable production conditions.
-
Environmental responsibility: Efficient heat exchange reduces carbon emissions and aligns with sustainability targets.
-
Operational safety: Controlling heat flow prevents equipment damage and overheating hazards.
-
Economic impact: Industries benefit from reduced energy consumption and longer equipment lifespan.
Industries that rely heavily on heat exchangers include petrochemical plants, refineries, food processing, power generation, pharmaceuticals, and refrigeration systems. These sectors depend on temperature management to maintain product quality and operational safety.
Recent Updates
Between 2024 and 2025, several advancements have reshaped the industrial heat exchanger market and its applications:
-
Adoption of compact and microchannel designs (2024): These models enhance heat transfer performance while reducing equipment size, making them ideal for modern, space-efficient plants.
-
Integration of IoT and AI (2025): Smart sensors and predictive monitoring systems now enable real-time data analysis, optimizing performance and maintenance scheduling.
-
Sustainable materials (2025): Advances in corrosion-resistant alloys and composite materials have improved durability and reduced environmental impact.
-
Additive manufacturing (3D printing): Rapid prototyping and custom part production are now common in exchanger design, enabling more precise configurations.
-
Heat recovery systems: More industries are adopting heat recovery exchangers to meet energy efficiency goals and reduce carbon emissions.
A 2025 industry report predicts steady growth in the heat exchanger market, driven by global sustainability initiatives and increasing demand for energy-efficient industrial systems.
Laws or Policies
Industrial heat exchangers are regulated under various national and international standards to ensure safety, efficiency, and environmental compliance. These regulations help maintain uniform design, operation, and testing standards across industries:
-
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (USA): Governs the design, manufacture, and inspection of heat exchangers that operate under pressure.
-
European Pressure Equipment Directive (PED): Ensures compliance for heat exchangers within the European Union, focusing on safety and performance.
-
ISO Standards: ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 cover quality management and environmental responsibility in heat exchanger production.
-
EPA and EU Emission Regulations: Encourage the use of energy-efficient systems to minimize greenhouse gas emissions and energy waste.
-
Energy Efficiency Programs (2025): Many countries now incentivize industries that adopt heat recovery and sustainable exchanger technologies as part of climate action initiatives.
These laws ensure that industrial heat exchangers meet high safety and environmental benchmarks, supporting global efforts toward cleaner industrial operations.
Tools and Resources
Several digital and educational tools help engineers, operators, and students understand and manage industrial heat exchangers more effectively:
-
Heat Exchanger Design Calculators: Online calculators help determine required surface area, flow rate, and efficiency based on operating parameters.
-
Simulation Software: Tools like ANSYS Fluent, Aspen HYSYS, and COMSOL Multiphysics enable simulation of fluid dynamics and thermal performance.
-
Maintenance Management Systems: IoT-based platforms provide real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance alerts, and performance tracking.
-
Technical Standards Databases: Organizations like ASME, ISO, and ASTM provide downloadable specifications for compliance and design.
-
Educational Resources: Engineering portals and online courses explain the fundamentals of heat transfer, exchanger design, and system optimization.
Example Table: Common Types of Industrial Heat Exchangers and Their Applications
| Type of Heat Exchanger | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Shell and Tube | Fluid flows through tubes inside a shell | Oil refineries, power plants |
| Plate Heat Exchanger | Thin metal plates transfer heat efficiently | HVAC, food processing |
| Air-Cooled | Uses air to cool fluids instead of water | Power generation, refrigeration |
| Double Pipe | Two concentric pipes for heat exchange | Chemical processing, small systems |
| Spiral Heat Exchanger | Compact spiral channels for viscous fluids | Wastewater treatment, pulp industries |
FAQs
What is the main function of an industrial heat exchanger?
Its primary function is to transfer heat between two fluids without mixing them, maintaining desired temperatures in industrial systems efficiently and safely.
What are the most common types of industrial heat exchangers?
The most common types include shell and tube, plate, air-cooled, and double-pipe exchangers, each suited to specific applications and fluid types.
How do smart heat exchangers improve efficiency?
Smart exchangers use IoT sensors and AI algorithms to monitor temperature, flow, and pressure in real time, allowing predictive maintenance and improved energy use.
Are heat exchangers environmentally friendly?
Yes. By recycling heat energy and reducing fuel consumption, they lower carbon emissions and support industrial sustainability efforts.
What factors affect heat exchanger performance?
Key factors include flow rate, temperature difference, fluid properties, fouling (build-up inside the exchanger), and material thermal conductivity.
Conclusion
Industrial heat exchangers are the backbone of energy-efficient and sustainable industrial operations. Their ability to manage and recover heat ensures optimal performance, reduced energy waste, and lower emissions.
In 2025, the focus on digital innovation, sustainability, and regulatory compliance continues to redefine how these systems are designed and managed. From compact designs to AI-powered monitoring, the evolution of heat exchangers reflects the broader global shift toward smarter, greener technologies.





