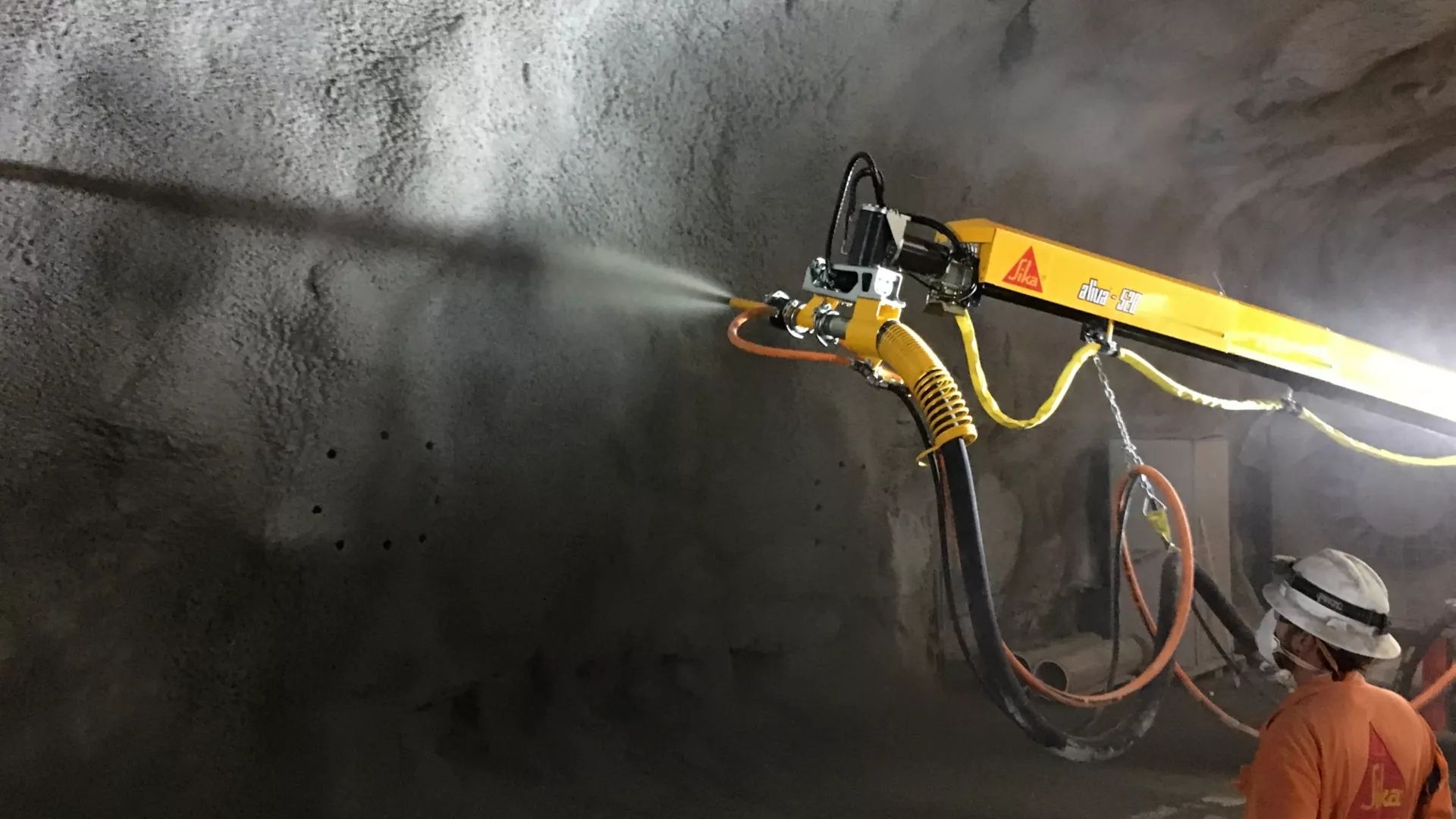
Shotcrete Machines Explained: Key Insights and Technical Details You Should Know
Shotcrete machines are specialized equipment used to project concrete at high velocity onto surfaces, such as tunnel walls, slopes, and structural reinforcements. The process, known as shotcreting or sprayed concrete, was developed in the early 20th century and has since become essential in modern construction and civil engineering.
Unlike traditional poured concrete, shotcrete is applied pneumatically using compressed air. This method allows concrete to adhere to irregular or vertical surfaces without formwork. Shotcrete machines exist to meet the demand for fast, durable, and efficient concrete application in projects such as tunnels, bridges, swimming pools, and retaining walls.
Shotcrete application can be divided into two main methods:
-
Dry-mix shotcrete: Dry material is mixed with water at the nozzle.
-
Wet-mix shotcrete: Pre-mixed concrete is pumped through the hose and sprayed directly.
Both methods use similar equipment but differ in mixing technique and suitability for specific projects.

Importance
Shotcrete machines are vital to modern construction because they enhance efficiency, durability, and design flexibility. Their importance can be understood through the following points:
-
Structural integrity: Shotcrete provides strong bonding and high compressive strength, essential for tunnels and slope stabilization.
-
Efficiency: The spraying technique reduces construction time and minimizes formwork requirements.
-
Versatility: Can be applied to vertical, overhead, and curved surfaces that would be difficult to reach using traditional pouring methods.
-
Repair and maintenance: Ideal for reinforcing existing structures, repairing damaged concrete, and adding protective coatings.
-
Cost efficiency and resource optimization: Shotcrete machines reduce material waste and improve project timelines.
Industries most impacted include mining, civil infrastructure, hydropower, and underground construction. Workers, engineers, and contractors rely on shotcrete for its reliability in challenging environments such as tunnels or mountainous regions.
Recent Updates
From 2024 to 2025, several notable advancements have occurred in shotcrete technology:
-
Automation and robotics (2025): Remote-controlled robotic arms equipped with shotcrete nozzles are increasingly used in tunnel projects, improving safety and precision.
-
Eco-friendly shotcrete formulations (2024): Manufacturers are developing low-carbon cement mixes and recycled aggregate materials to reduce environmental impact.
-
Digital monitoring and control (2024): Modern shotcrete machines now feature digital panels and IoT sensors for real-time pressure, flow rate, and temperature monitoring.
-
Fiber-reinforced shotcrete (2025): New fiber-reinforced mixtures enhance tensile strength and crack resistance, particularly in seismic regions.
-
Improved pump technology (2025): Dual-piston pumps and variable flow systems allow smoother and more consistent concrete application.
Industry reports predict that automation, sustainability, and digital integration will remain the top three trends influencing the global shotcrete market through 2030.
Laws or Policies
Shotcrete applications are subject to regulations that ensure safety, structural reliability, and environmental compliance. These standards vary by country but share common principles:
-
Occupational safety standards: Agencies like the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA) regulate the operation of shotcrete machines to minimize risks from high-pressure systems and airborne materials.
-
Building and material codes: Standards such as ACI 506R (Guide to Shotcrete) and EN 14487 (Sprayed Concrete Specification) provide detailed guidance on materials, mixing, and application.
-
Environmental regulations: Laws related to dust suppression, water runoff, and cement emissions influence shotcrete practices, especially in urban construction zones.
-
Certification and training requirements: Operators in many countries must complete safety and technical training programs to ensure proper handling of high-pressure shotcrete systems.
Governments worldwide encourage adherence to sustainable and safe construction practices, making compliance with these regulations essential for any large-scale infrastructure project.
Tools and Resources
A variety of tools and digital platforms support engineers and operators in using shotcrete machines effectively:
-
Mix design calculators: Online tools to determine water-cement ratios, fiber content, and nozzle pressure.
-
Flow rate monitoring systems: Digital interfaces or mobile apps that record shotcrete volume and application speed.
-
Simulation software: Programs such as ANSYS and COMSOL Multiphysics can model the spray pattern and mechanical performance of shotcrete layers.
-
Training platforms: Online courses by the American Concrete Institute (ACI) and International Tunnelling Association (ITA) offer technical guidance on modern shotcrete techniques.
-
Inspection templates: Checklists for pre-operation safety, material testing, and post-application quality control.
FAQs
What is the difference between dry-mix and wet-mix shotcrete?
Dry-mix shotcrete adds water at the nozzle, giving operators more control over moisture content. Wet-mix shotcrete uses pre-mixed concrete, providing consistent quality and less rebound loss.
Where are shotcrete machines most commonly used?
They are widely used in tunnel linings, slope stabilization, swimming pool construction, and underground mining for ground support.
How is shotcrete different from traditional concrete?
Shotcrete is sprayed through a nozzle under high air pressure, allowing application on vertical or overhead surfaces without formwork. Traditional concrete requires molds or forms for placement.
Are there environmental benefits to using modern shotcrete?
Yes. New formulations use recycled materials and low-carbon cement alternatives. Efficient application also reduces waste and water consumption.
What safety precautions are necessary when operating shotcrete machines?
Operators should wear protective gear, avoid direct exposure to high-pressure spray, and ensure proper ventilation to reduce dust and rebound hazards.
Example Table: Comparison of Dry-Mix and Wet-Mix Shotcrete
| Feature | Dry-Mix Shotcrete | Wet-Mix Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Water addition method | At nozzle | Pre-mixed in hopper |
| Control over moisture | High | Moderate |
| Rebound (waste material) | Higher | Lower |
| Application consistency | Operator dependent | More uniform |
| Common use | Repair, small-scale projects | Large structures, tunnels |
Conclusion
Shotcrete machines represent one of the most important advancements in concrete technology, providing durable, fast, and adaptable construction solutions. They have transformed how engineers build tunnels, stabilize slopes, and repair structures—combining mechanical precision with material science.
As automation, sustainability, and digital monitoring continue to evolve, shotcrete applications are becoming safer and more efficient. Adherence to global standards and environmental guidelines ensures that this technology remains a trusted method for both modern infrastructure and rehabilitation projects.