Discover How Plastic Injection Machines Improve Manufacturing Results
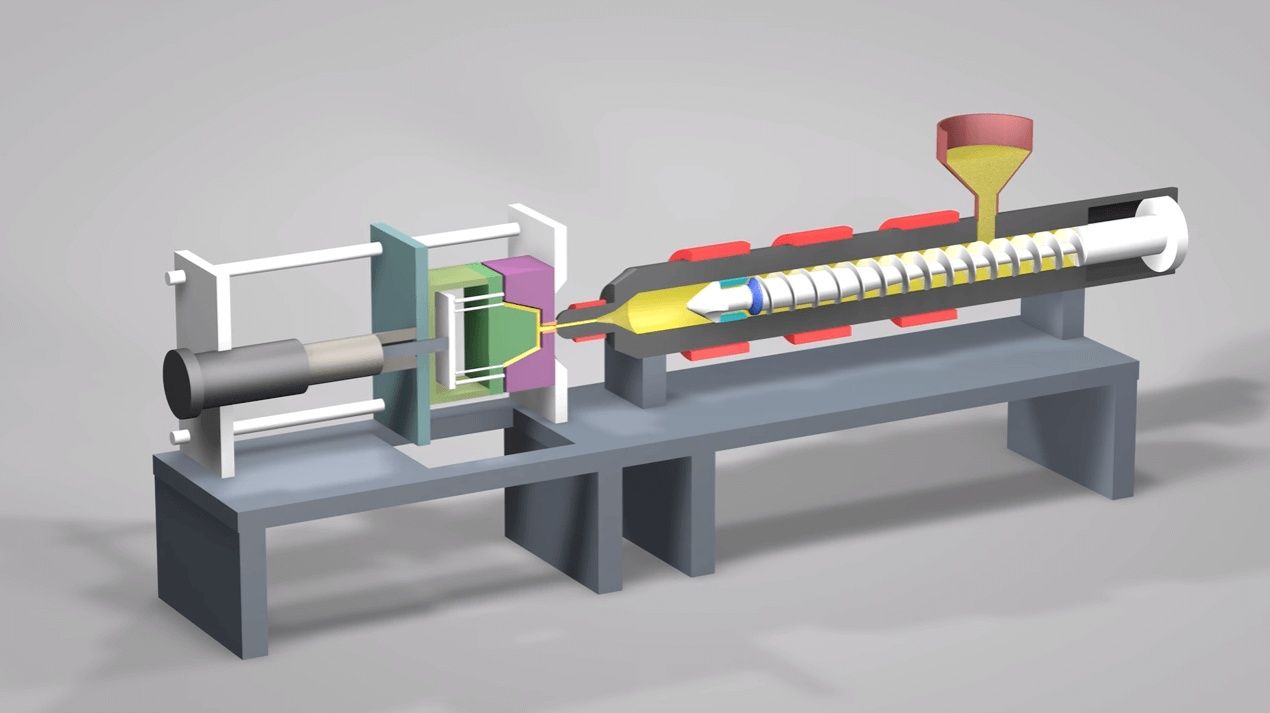
Plastic injection machines are industrial tools designed to shape molten plastic into usable components by forcing it into a precise mold. This technology exists because many industries—such as packaging, automotive, electronics, healthcare, and consumer goods—require large volumes of identical parts with high accuracy.
Before injection molding became common, manufacturers relied on manual shaping or slower forming methods. With the rise of mass production, companies needed a faster and more consistent way to produce plastic components. Injection machines solved this need by offering:
-
Controlled heating and cooling
-
Repeatable molding cycles
-
Compatibility with diverse plastic materials
-
High accuracy and minimal waste
Over time, injection machines evolved from manual systems to fully automated and computer-controlled equipment. Today, they are central to modern manufacturing lines.
Importance – Why Plastic Injection Machines Matter Today
Injection machines play a major role in manufacturing efficiency and product quality. Their importance comes from several factors:
1. Consistency in Production
These machines create identical components across thousands or millions of cycles. Industries rely on this to maintain product quality and safety.
2. Faster Manufacturing
An injection cycle can take only a few seconds, allowing companies to rapidly scale production.
3. Material Efficiency
The process reduces waste, as excess plastic can often be recycled and reused.
4. Lower Manufacturing Costs
Automation reduces labor requirements and minimizes defects, helping companies control costs.
5. Support for Complex Designs
The machines can shape intricate patterns, thin-wall structures, or detailed surfaces with precision.
6. Impact on Many Sectors
Industries affected include:
-
Automotive (dashboards, clips, handles)
-
Medical (syringe parts, casings, safety components)
-
Packaging (caps, containers, closures)
-
Electronics (enclosures, switches)
-
Household products (toys, containers, tools)
Injection molding solves problems like slow production, inconsistent shapes, and high manufacturing waste.
Recent Updates – Trends and Changes in the Last Year
The injection molding industry continues to evolve with new technologies and sustainability priorities. Some notable updates include:
1. Rise of Electric Injection Machines (2024–2025)
Electric machines are becoming more widely adopted due to their lower energy consumption compared to hydraulic systems. This shift grew significantly through 2024 as factories aimed to reduce operational costs.
2. Increased Use of Recycled Plastics
Environmental policies encouraged more recyclability. Many machine builders introduced systems optimized for recycled resins in 2024, improving melt stability and consistency.
3. Smart Factory Integration
Automation advances in 2024–2025 brought:
-
AI-assisted process monitoring
-
Real-time data tracking
-
Predictive maintenance systems
These reduce downtime and improve product quality.
4. Multi-Material Molding Growth
Demand increased for products that combine different materials—such as soft-touch grips or multi-color components. Systems with multi-shot capabilities became more common in 2024.
5. Safety Upgrades
New machine designs now include improved guarding, emergency control logic, and operator training guidelines.
Laws or Policies – Regulations Affecting Plastic Injection Machines
Regulations vary by country, but several general policies influence how these machines are used:
1. Environmental and Waste Management Laws
Many regions have laws limiting plastic waste and encouraging recycling:
-
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs
-
Limits on single-use plastics
-
Recycling content requirements
These policies encourage manufacturers to optimize processes and reduce waste.
2. Safety Standards for Machinery
Most countries follow machine safety rules such as:
-
ISO 20430:2020 for injection molding machine safety
-
National occupational safety regulations
-
Electrical safety standards for industrial equipment
These ensure that machines protect workers and operate safely.
3. Energy Efficiency Regulations
Some regions offer incentives for switching to energy-efficient electric injection machines.
4. Quality Standards
Industries such as food packaging, medical devices, and automotive parts require compliance with:
-
FDA guidelines (for food-contact plastics)
-
ISO 13485 (for medical products)
-
IATF 16949 (for automotive production)
Injection machines must support precise and traceable production to meet these requirements.
Tools and Resources – Helpful Platforms and Services
These tools and resources support selection, operation, and optimization of injection machines:
Software Tools
-
Moldflow (Autodesk) – Simulation software for mold design
-
SolidWorks Plastics – Material flow analysis inside molds
-
Trelleborg Material Selector – Helps pick compatible compounds
-
IQMS Manufacturing ERP – Manages production data
Calculators
-
Plastic Injection Cycle Time Calculator
-
Melt Flow Rate Calculator
-
Clamp Force Calculator
-
Cooling Time Estimator
Websites and Knowledge Platforms
-
PlasticsToday – Industry news and updates
-
Plastics Technology Magazine – Guides and trend reports
-
SPI (Plastics Industry Association) – Standards and resources
-
Material data sites like UL Prospector – Plastic material database
Training Resources
-
YouTube technical tutorials
-
Online molding certification programs
-
Industry webinars on efficiency and mold design
Table: Comparison of Injection Machine Types
| Machine Type | Key Feature | Best For | Energy Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic | High power | Large parts | High |
| Electric | High precision, efficient | Small-medium parts | Low |
| Hybrid | Mix of power & efficiency | Wide applications | Medium |
FAQs
1. What materials can be used in plastic injection machines?
Most thermoplastics can be used, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, ABS, PVC, nylon, and polycarbonate. Material selection depends on the product’s strength, heat resistance, and flexibility requirements.
2. How long does an injection molding cycle take?
Cycle times vary based on mold complexity, part thickness, and cooling time. Simple parts may take 5–10 seconds, while complex ones may take 30 seconds or longer.
3. Are electric injection machines better than hydraulic ones?
Electric machines offer improved energy efficiency and precision, while hydraulic systems are still preferred for large and high-force applications. The choice depends on the product and production scale.
4. What factors affect mold quality?
Mold design, material selection, temperature control, cooling channels, and machine settings all influence final product accuracy and surface finish.
5. Can recycled plastic be used in injection molding?
Yes, many recycled resins work well, but adjustments may be needed to control melt quality, moisture content, and color variation.
Final Thoughts
Plastic injection machines are essential to modern manufacturing, enabling companies to produce consistent, high-quality parts quickly and efficiently. Their role continues to grow as industries adopt automation, recycled materials, and energy-efficient technologies. Understanding how these machines work and the policies, tools, and industry updates around them helps manufacturers make informed decisions that support quality, compliance, and long-term sustainability.






