Discover How Engine Assembly Machines Improve Production Accuracy
Engine assembly machines are specialized systems used to assemble internal combustion engines and other power units in a controlled, repeatable, and precise manner. These machines support tasks such as component positioning, torque application, bearing installation, piston fitting, crankshaft alignment, and fastening operations. They are widely used in automotive manufacturing, industrial engine production, and equipment assembly facilities.
Historically, engine assembly relied heavily on manual labor. Skilled technicians assembled engines using hand tools and visual checks. While effective at smaller scales, manual assembly became increasingly difficult as engine designs grew more complex and production volumes increased. Small variations in torque, alignment, or component placement could lead to performance issues, premature wear, or failure.
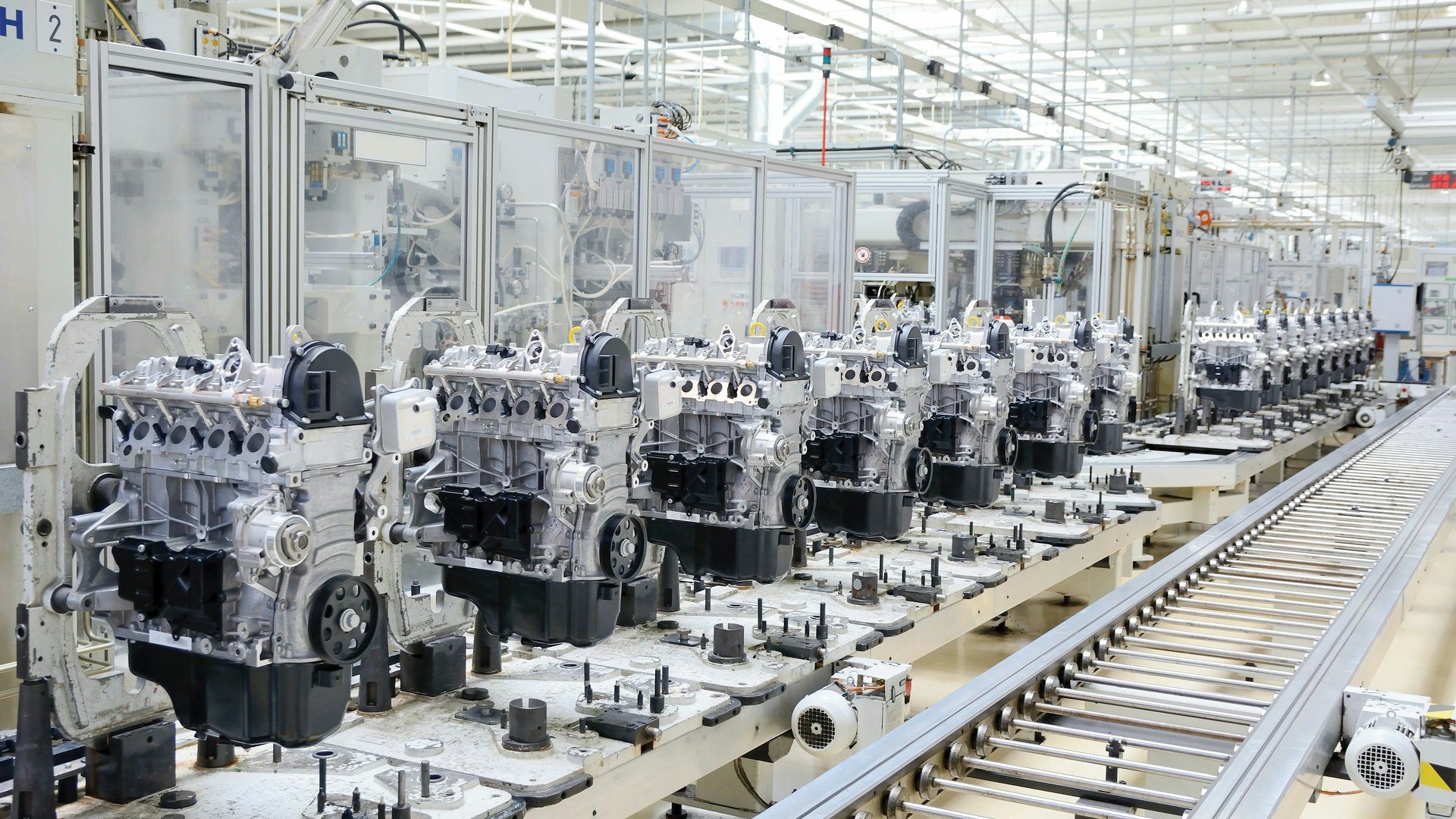
Engine assembly machines were developed to address these challenges. By automating and standardizing critical assembly steps, these machines help ensure that every engine is built to consistent specifications. Over time, they became essential for maintaining quality, reducing variability, and meeting modern production demands.
Importance – Why Engine Assembly Machines Matter Today
Engine assembly machines play a key role in achieving accuracy, consistency, and efficiency in manufacturing.
Improves Production Accuracy
Machines apply precise torque, alignment, and positioning, reducing human error.
Ensures Consistent Quality
Standardized processes ensure each engine meets the same specifications.
Reduces Rework and Scrap
Accurate assembly lowers the risk of defects that require disassembly or replacement.
Supports Higher Production Volumes
Automation enables faster assembly without sacrificing quality.
Enhances Worker Safety
Machines handle heavy components and repetitive tasks, reducing physical strain.
Benefits Multiple Stakeholders
Engine assembly machines support:
-
Automotive and engine manufacturers
-
Quality control teams
-
Production engineers
-
Maintenance and operations staff
Solves Common Manufacturing Challenges
Effective engine assembly helps address:
-
Inconsistent torque application
-
Misaligned components
-
Assembly-related failures
-
High rejection rates
-
Production bottlenecks
In competitive manufacturing environments, accuracy directly impacts reliability and cost control.
Recent Updates – Trends and Developments in 2024–2025
Engine assembly technology has continued to evolve over the past year, driven by digitalization and efficiency goals.
Increased Use of Smart Assembly Systems (2024)
Manufacturers adopted systems with built-in sensors to monitor torque, force, and position in real time.
Integration with Manufacturing Execution Systems
Assembly machines increasingly connected to MES platforms for traceability and reporting.
Expansion of Modular Assembly Lines
Flexible machine designs allowed faster adaptation to different engine variants.
Improved Error Detection and Feedback
Machines provided immediate alerts when assembly parameters were outside tolerance.
Support for Hybrid and Alternative Powertrains
Assembly systems were adapted to handle components used in hybrid and low-emission engines.
Focus on Data-Driven Quality Control
Production data from assembly machines was used to analyze trends and prevent defects.
These developments highlight a shift toward intelligent, connected, and adaptable assembly environments.
Laws or Policies – Regulations Affecting Engine Assembly
Engine assembly machines operate within regulatory frameworks related to safety, quality, and environmental standards.
Manufacturing Safety Regulations
Machines must comply with workplace safety standards to protect operators.
Quality Management Standards
Many manufacturers follow ISO-based quality systems that require consistent and documented assembly processes.
Environmental and Emission Policies
Accurate engine assembly supports compliance with emission performance requirements.
Product Liability Regulations
Consistent assembly helps reduce the risk of defects that could lead to recalls or legal issues.
Machine Certification and Compliance
Assembly equipment must meet electrical, mechanical, and operational safety certifications.
Adhering to these regulations ensures safe, compliant, and reliable production operations.
Tools and Resources – Helpful Support for Engine Assembly Accuracy
A range of tools and resources support effective use of engine assembly machines.
Useful Tools and Resources
| Tool / Resource | Purpose / Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automated Torque Tools | Ensure precise fastening |
| Vision Inspection Systems | Verify component placement |
| Force and Position Sensors | Monitor assembly accuracy |
| Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) | Track assembly data |
| Calibration Equipment | Maintain machine accuracy |
| Assembly Process Checklists | Standardize workflows |
| Operator Training Modules | Improve machine handling |
| Performance Dashboards | Monitor accuracy metrics |
These resources help maintain consistent quality throughout production.
FAQs – Clear and Factual Answers
What are engine assembly machines?
They are automated or semi-automated systems used to assemble engine components accurately and consistently.
How do engine assembly machines improve accuracy?
They control torque, alignment, and positioning within defined tolerances.
Are engine assembly machines used only in large factories?
They are most common in large-scale manufacturing but can also be used in specialized or smaller operations.
Can engine assembly machines handle different engine models?
Many modern systems are modular and adaptable to multiple variants.
Do these machines replace human workers entirely?
No. They support workers by automating critical tasks while operators oversee and manage the process.
Final Thoughts
Engine assembly machines are a vital component of modern manufacturing, helping producers achieve high levels of accuracy and consistency. As engine designs become more complex and quality expectations rise, manual assembly alone is no longer sufficient. Recent advances in smart systems, data integration, and flexible assembly lines have further strengthened the role of these machines. When combined with proper training, compliance practices, and continuous monitoring, engine assembly machines support reliable production, reduced defects, and long-term manufacturing efficiency.





