Electrical Discharge Machining operates on a simple principle: controlled electric sparks melt and vaporize material from a workpiece. Instead of using mechanical force, EDM relies on thermal energy. The cutting tool and workpiece must not touch each other; instead, the spark discharge bridges the gap through a dielectric fluid, gradually shaping the material.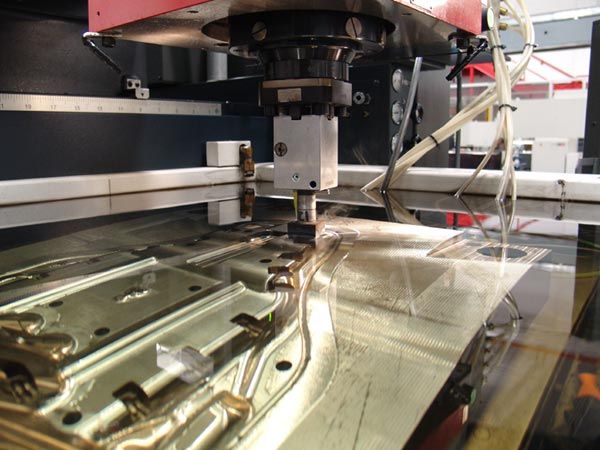
This process exists because many industries work with metals like titanium, nickel alloys, tool steel, and carbide. Traditional machining techniques often face challenges such as tool wear, poor finish, or inability to handle complex shapes. EDM solves these issues by enabling:
-
High dimensional accuracy
-
Machining of hardened materials
-
Creation of complex profiles and micro-features
-
Minimal mechanical stress on components
As manufacturing sectors began moving towards miniaturization, precision engineering, and advanced product design, EDM established itself as a reliable solution for tasks that require extreme detail and repeatability.
Importance – Why EDM Matters in Modern Manufacturing
In industries where accuracy, surface finish, and tolerance levels are critical, EDM has a significant role. Aerospace firms use EDM for turbine blade cooling channels and high-performance components. Medical device makers depend on EDM for implants, surgical instruments, and tiny components used in electronic health devices. The automotive sector applies EDM for engine components, injection molds, and calibration parts.
The core importance of EDM today is linked to needs such as:
-
Precision machining for aerospace and defense
-
Micro-manufacturing for electronics
-
Mold and die development for mass production
-
Research and prototyping in product development
EDM supports sectors where accuracy directly influences performance and safety. It reduces material stress, maintains geometry quality, and helps produce consistent parts where other methods would require multiple finishing stages.
Recent Updates and Trends
The past year saw significant movement in the EDM landscape, especially in automation, AI-based monitoring, and thermal efficiency improvements. In 2024 and 2025, new trends emerged, including adaptive discharge control, integration with CAD/CAM software, and multi-axis optimization. These developments allow machines to learn material behaviors, reduce spark inefficiencies, and improve tool wear patterns.
Key trends shaping EDM:
| Advancement | Impact on Application |
|---|---|
| High-speed EDM systems | Faster material removal with improved precision |
| AI-based machining control | Predictive spark regulation and reduced human input |
| Energy-efficient generators | Lower power consumption and less thermal distortion |
| Micro-EDM technology | Precision machining for medical implants and MEMS |
| Hybrid EDM + CNC combinations | Larger component compatibility and automation |
Robotic loading and monitoring systems are also becoming common in smart factories, allowing uninterrupted machining cycles. Manufacturers are investing in wire EDM for intricate cutting and sinker EDM for mold cavities and deep-hole machining.
Laws, Regulations, and Policy Influence
Electrical Discharge Machining is subject to machine safety regulations, workplace compliance standards, and environmental rules related to dielectric fluid disposal. Many governments encourage adoption of precision machining under programs promoting modern manufacturing and export-ready production units. Factories using EDM must follow national guidelines for worker protection such as electrical shielding, spark exposure control, and proper ventilation systems.
Policies influencing EDM operations generally include:
-
Machine tool certification and compliance standards
-
Worksite electrical safety rules
-
Industrial waste and dielectric fluid disposal regulations
-
Export-grade production quality requirements for aerospace and medical components
Countries with manufacturing-focused initiatives encourage technological upgrades, including the use of high-precision equipment for mold making, automotive tooling, and component development. This supports innovation and global manufacturing competitiveness.
Tools, Resources, and Helpful Platforms
People learning or working with EDM benefit from technical tools, calculation utilities, and reference libraries. Industry resources help in modeling spark erosion, estimating machining time, and planning electrode selection.
Useful resources include:
-
EDM parameter calculators for pulse rate, spark gap, and erosion cycle estimation
-
CAD/CAM software for part modeling and path simulation
-
Material hardness charts for selecting suitable machining settings
-
Surface finish comparators for tolerance measurement
-
Electrical Discharge Machining reference journals and research papers
Additional learning platforms provide machining design guidelines, study modules on spark erosion physics, and standards for electrode copper, graphite, or tungsten materials. A dedicated planner or template is useful for recording machining parameters such as discharge current, voltage, and electrode wear rate for repeatability.
FAQs – Common Questions Answered Clearly
What materials can be machined with EDM?
EDM works primarily on electrically conductive materials. Hardened steel, titanium, tool steel, carbide, and nickel alloys respond well to spark erosion. Non-conductive materials cannot be processed directly using EDM.
What are the main types of EDM?
The most recognized types are Wire EDM for profile cutting, Sinker EDM for cavity creation, and Hole-Drilling EDM for micro-perforation. Each type serves different applications based on shape complexity and material thickness.
Does EDM affect the mechanical strength of a component?
Material removal occurs through thermal melting, which may leave a heat-affected surface layer. Finishing passes, flushing, or polishing typically help maintain the designed strength and surface integrity.
Is EDM suitable for large production runs?
It can support both volume and prototype machining. Consistent tolerances make it useful for repeated components, especially in mold and die industries. Production speed depends on spark rate, electrode design, and machine parameters.
How does EDM differ from traditional machining?
Traditional machining uses cutting tools, while EDM removes material through electrical discharge. This allows machining of hardened metals and intricate shapes without physical tool pressure.
Conclusion
Electrical Discharge Machining stands as a crucial technology in modern precision engineering. It enables the shaping of complex materials that cannot be processed through conventional methods. Over the years, EDM has evolved with innovations such as AI-based spark control, high-speed discharge systems, and micro-manufacturing capabilities. Regulations ensure safe machine operation and responsible handling of dielectric fluids, while digital tools and reference platforms support users in understanding settings and material behaviors.
Understanding EDM offers value for anyone working in product design, aerospace, automotive, medical engineering, or mold development. Its role continues to grow as industries evolve toward precision-driven manufacturing and advanced component engineering.