Aviation is a highly regulated field because aircraft operation involves passenger safety, national airspace coordination, and international standards. Pilot training exists to maintain uniform safety levels across civil aviation while preparing individuals for various flying environments, including commercial, cargo, charter, and private aviation.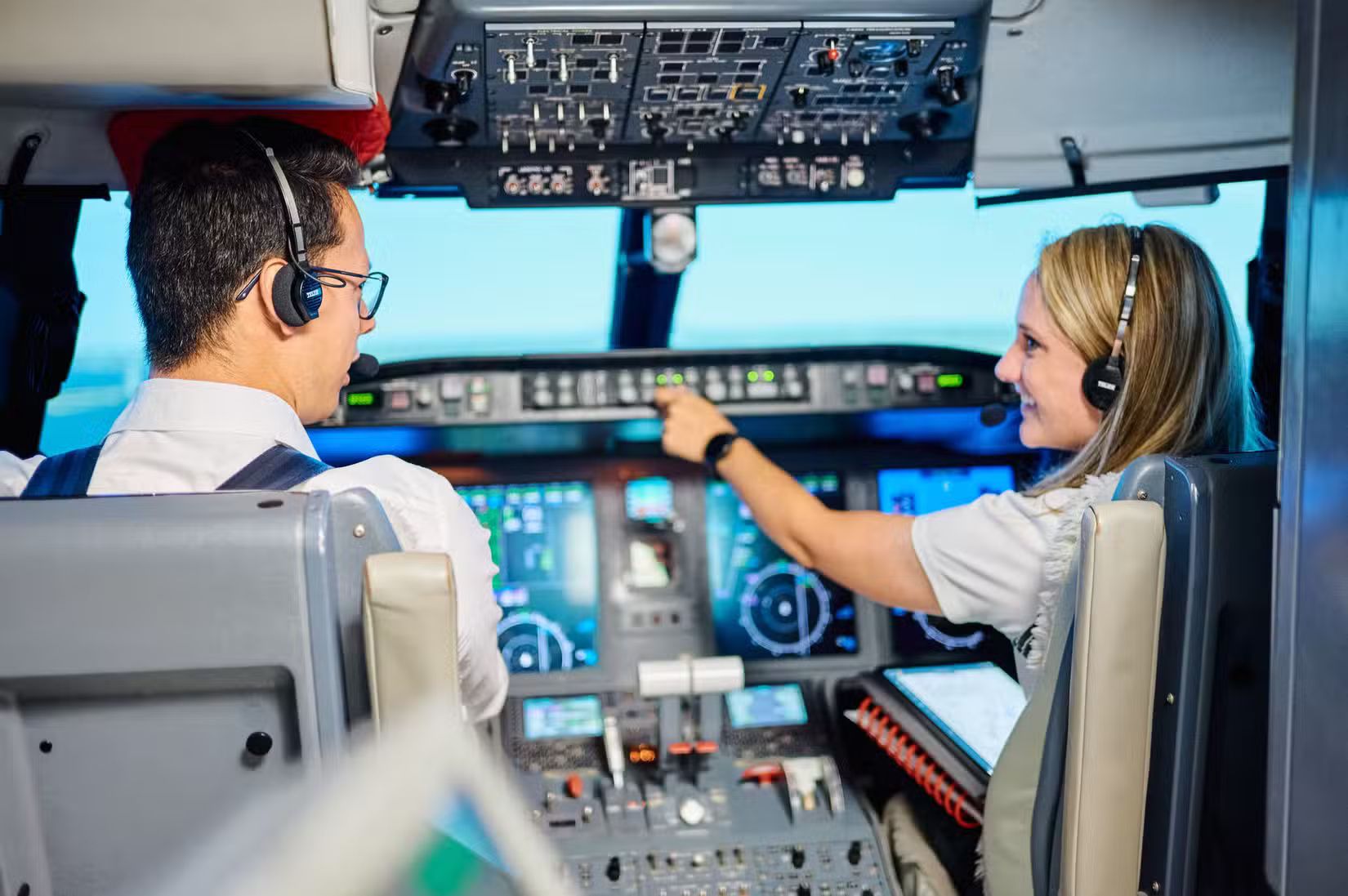
Training pathways are designed to build knowledge progressively, starting with aviation fundamentals and advancing toward complex aircraft handling and navigation techniques.
Why Pilot Training Matters in the Modern Aviation Landscape
Global air travel continues to grow as economies expand and international connectivity increases. This growth requires well-trained pilots who can operate advanced aircraft systems safely and efficiently.
Pilot training matters because it:
-
Supports aviation safety across domestic and international routes
-
Prepares pilots to manage advanced cockpit technology
-
Helps maintain standardized flying procedures worldwide
-
Reduces human error through structured learning and simulation
-
Enables efficient air traffic coordination
-
Strengthens emergency preparedness and decision-making
Pilot training affects a wide range of stakeholders, including passengers, airlines, airports, air traffic controllers, aviation regulators, and aircraft manufacturers. Proper training ensures that flight operations remain reliable even in challenging weather, congested airspace, or technical irregularities.
In modern aviation, pilots are not only aircraft operators but also system managers who monitor automation, communicate with multiple authorities, and make real-time decisions.
Recent Developments and Industry Trends
Pilot training has evolved significantly over the past year due to technological advancements and regulatory updates.
Key developments observed during 2024–2025 include:
-
Expanded use of full-motion flight simulators for advanced scenario training
-
Increased focus on automation management and human–machine interaction
-
Greater emphasis on evidence-based training models
-
Integration of data analytics to assess pilot performance patterns
-
Enhanced training modules for adverse weather and abnormal operations
-
Growing use of digital learning platforms for ground theory instruction
In 2024, aviation authorities across multiple regions updated competency-based training frameworks to align pilot skills with real-world operational challenges rather than hours-based progression alone. This approach focuses on demonstrated capability, situational awareness, and decision-making quality.
Environmental awareness has also become a part of modern pilot education, including fuel-efficient flying techniques and emissions-conscious operational practices.
Laws, Regulations, and Policy Framework
Pilot training is governed by strict aviation regulations to ensure global safety and standardization. Rules differ by country but generally follow international guidelines.
In many countries, pilot training falls under the authority of national aviation regulators aligned with international frameworks such as those recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
Common regulatory aspects include:
-
Medical fitness requirements for pilots
-
Mandatory theoretical and practical training hours
-
Standardized flight skill assessments
-
Aircraft type-specific certification
-
Ongoing proficiency checks and recurrent training
-
Airspace rules and operational limitations
For example, in India, pilot training and licensing are regulated by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), which defines curriculum structure, examination standards, medical criteria, and flight testing procedures.
Regulations ensure that pilots trained in one country can safely operate in international airspace while maintaining consistent operational standards.
Learning Tools, Educational Resources, and Training Support
Pilot training relies on a combination of instructional tools, digital platforms, and reference materials that support both theoretical understanding and practical skill development.
Helpful resources commonly used include:
-
Aviation ground school manuals covering aerodynamics, meteorology, navigation, and air regulations
-
Computer-based training (CBT) modules for systems knowledge
-
Flight planning and navigation software for route analysis
-
Performance calculation tools for weight, balance, and fuel estimation
-
Weather briefing platforms for aviation forecasting
-
Flight simulators replicating real cockpit environments
-
Logbook templates for recording flight experience
-
Aeronautical charts and airspace maps
These tools help learners visualize complex concepts and prepare for real-world flight operations in a controlled learning environment.
Core Knowledge Areas Covered in Pilot Training
Pilot training focuses on building competence across multiple domains.
Key learning areas include:
-
Principles of flight and aircraft performance
-
Aircraft systems and instrumentation
-
Air navigation and flight planning
-
Meteorology and weather interpretation
-
Aviation communication procedures
-
Human performance and limitations
-
Emergency and abnormal situation handling
-
Operational safety and risk management
Training emphasizes understanding not just “how” to fly, but “why” certain procedures exist. This knowledge helps pilots adapt to unexpected situations rather than relying solely on memorized actions.
Comparison Table: Training Stages and Learning Focus
| Training Stage | Primary Focus | Learning Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Flight Phase | Aircraft handling and control | Fundamental flying skills |
| Intermediate Phase | Navigation and airspace use | Situational awareness |
| Advanced Phase | Instrument and system management | Precision and accuracy |
| Assessment Phase | Skill evaluation | Regulatory compliance |
Practical Insights for Learners
Effective pilot training requires discipline, consistency, and structured learning habits.
Helpful guidance includes:
-
Developing strong theoretical foundations before advanced flying
-
Maintaining accurate flight logs and study records
-
Practicing checklist discipline for every operation
-
Learning weather interpretation beyond basic forecasts
-
Understanding automation limits and manual flying balance
-
Reviewing flight data and instructor feedback regularly
-
Focusing on decision-making rather than speed
Successful trainees approach aviation as a continuous learning process rather than a fixed milestone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of pilot training?
The main objective is to ensure safe aircraft operation through structured knowledge, skill development, and regulatory compliance.
How long does pilot training usually take?
Training duration varies based on license type, training schedule, weather conditions, and individual learning pace.
Is simulator training important?
Yes. Simulators allow pilots to practice complex scenarios, emergencies, and system failures in a safe environment.
Do pilots need ongoing training after certification?
Yes. Recurrent training and periodic assessments are mandatory to maintain proficiency and regulatory compliance.
Why is aviation regulation so strict?
Aviation involves public safety, shared airspace, and international coordination, requiring uniform standards and oversight.
Conclusion
Pilot training forms the backbone of modern aviation safety and operational reliability. Through structured education, simulation, and practical experience, it prepares individuals to operate complex aircraft in diverse conditions. Training programs emphasize safety, knowledge depth, and decision-making rather than just flight hours.
As aviation technology evolves, pilot training continues to adapt by incorporating data-driven assessment, advanced simulation, and global regulatory alignment. Understanding the fundamentals, regulatory framework, and learning resources provides valuable clarity for anyone interested in aviation education.
Pilot training is not simply about flying an aircraft; it is about mastering responsibility, systems awareness, and disciplined judgment within one of the world’s most regulated and safety-critical industries.