EV Battery Recycling: Complete Guide, Insights & Key Information
The growth of electric vehicles has brought convenience, sustainability gains, and reduced dependence on fossil-based transport, but it has also introduced a new responsibility—managing used EV batteries. EV battery recycling refers to the process of collecting, dismantling, processing, and recovering valuable materials from lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles. As more EVs approach end-of-life usage, understanding how recycling works has become an essential topic in both environmental and industrial discussions.
The concept exists because electric vehicle batteries contain elements such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, copper, graphite, and manganese. These materials can be recovered and reused instead of being disposed of, helping reduce pressure on mining and raw material extraction. EV battery recycling forms a critical part of a circular energy economy, where resources are retained within the system for longer use. The aim is to limit environmental impact, promote sustainable mobility, and maintain material efficiency.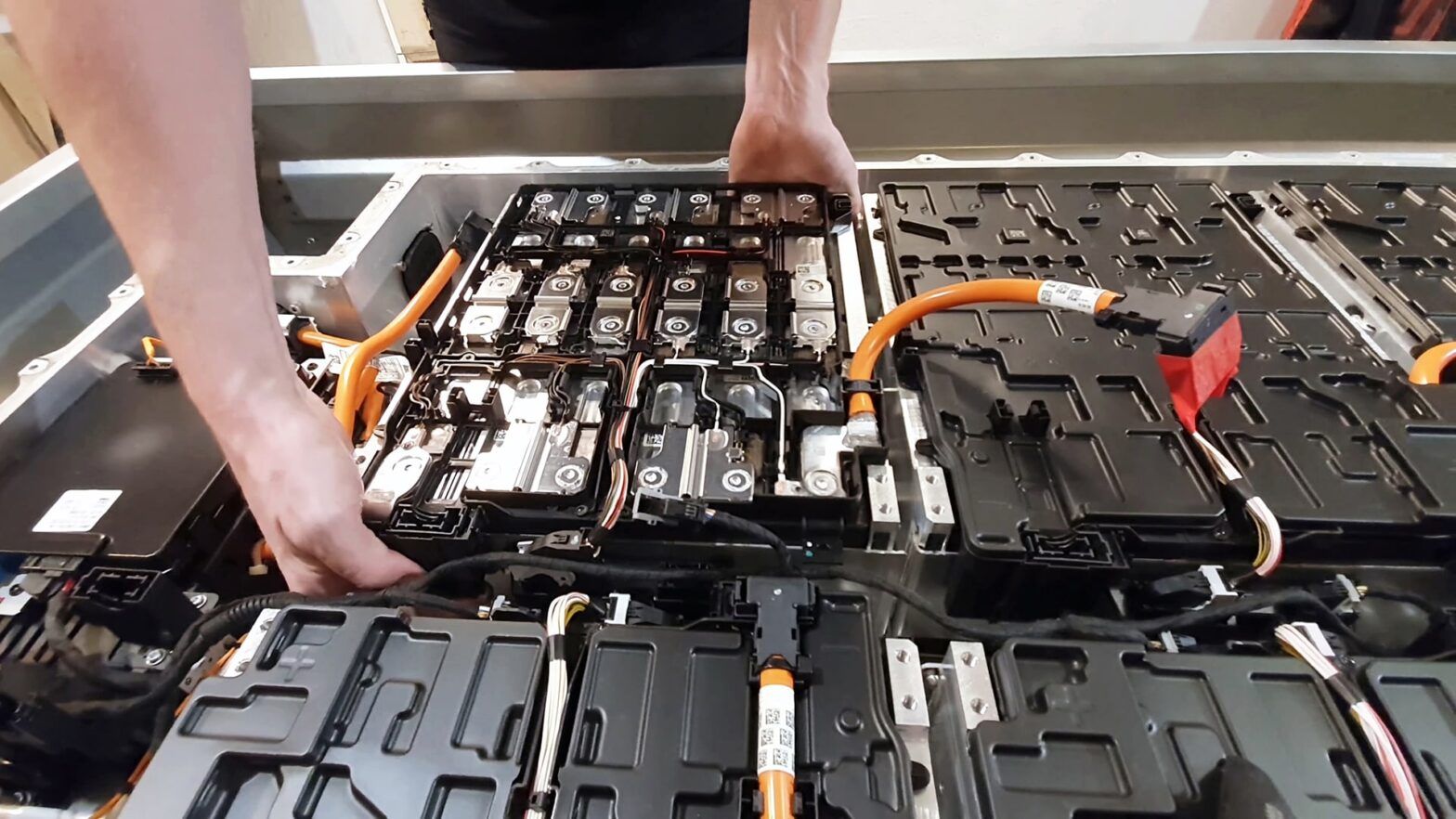
Why EV Battery Recycling Matters Today
EV adoption has accelerated globally in response to clean-energy goals, carbon-neutral transport, and growing awareness of air pollution challenges. As usage increases, so does the flow of end-of-life batteries, which require proper handling to avoid hazardous leakage. Recycling supports sustainability by reducing the demand for new lithium and cobalt extraction.
This topic involves many stakeholders:
-
Vehicle owners and fleet operators who eventually retire EV batteries
-
Automobile manufacturers working toward material reuse and circular lifecycle plans
-
Battery manufacturers and technologists developing second-life solutions
-
Governments and environmental planners attempting to reduce waste and emissions
-
Recycling and recovery facilities that process used and damaged units
The benefits of recycling include resource recovery, reduced landfill waste, and safer disposal of hazardous components. EV batteries contain electrolytes and metals that can be harmful if exposed to the environment. When recycling is implemented effectively, those risks decrease while valuable elements return to manufacturing systems.
Recent Updates: Trends, Technological Shifts, Market Developments
In the past year, EV battery recycling has drawn increased focus from sustainability groups, policy-makers, and automotive engineers. A few developments have shaped the direction of the industry:
-
2024 saw increased interest in closed-loop battery recycling, where recovered materials from used packs are fed directly back into the battery production chain. This approach reduces reliance on extraction and speeds up remanufacturing.
-
Thermal and hydrometallurgical extraction methods gained wider adoption in mid-2024, offering higher recovery rates of cobalt, lithium, and nickel at lower energy expenditure.
-
Research into solid-state battery recycling expanded in early 2025, as solid-state batteries move toward commercial scalability.
-
Several nations announced circular-economy strategies for EV components in late 2024, signaling long-term infrastructure planning for sustainable energy systems.
A simplified representation of material recovery potential:
| Material Recovered | Approximate Recovery Rate Trend |
|---|---|
| Lithium | Increasing with hydrometallurgy |
| Cobalt | High recovery efficiency |
| Nickel | Strong recovery value |
| Copper | Consistently high extraction |
| Graphite | Moderate recovery improvement |
These advances indicate that recycling technology is maturing, positioning electric mobility as more environmentally stable over time.
Policies, Guidelines, and Compliance Frameworks
EV battery recycling is often guided by national environmental and waste management regulations. Many countries require safe end-of-life handling and encourage sustainable processing pathways.
Typical policy approaches include:
-
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) frameworks holding manufacturers responsible for end-of-life collection
-
Hazardous waste handling protocols to ensure safe battery transport and dismantling
-
Recycling percentage targets, encouraging material recovery and reuse
-
Eco-design standards, motivating the creation of batteries that are simpler to disassemble and process
Regulatory oversight helps prevent improper disposal, supports material traceability, and ensures that recovered metals are handled in controlled facilities.
Tools, Platforms & Resources for Learning and Planning
Several resources help individuals, researchers, and analysts understand recycling processes, technology comparisons, and sustainability metrics. These include:
Industry Information & Technical Knowledge
-
Research papers published through environmental journals
-
Battery manufacturing whitepapers and lifecycle assessment reports
-
Automotive energy storage studies and recycling forecasts
Digital Tools & Software
-
EV battery lifecycle analysis models
-
Material flow calculators for circular-economy evaluation
-
Emission comparison tools for battery recovery and reuse
Knowledge-Based Directories
-
Maps of certified recycling facilities
-
Database of global sustainability policy frameworks
-
Technical resources on lithium-ion chemistry and recovery science
These resources support informed decision-making, technical planning, and environmental impact evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do EV batteries typically last before recycling?
An EV battery generally lasts several years before reaching reduced performance. Many units are reused for energy storage before being recycled when no longer viable.
What materials are most commonly recovered?
Recycled EV batteries usually yield lithium, nickel, cobalt, copper, aluminum, and graphite. These elements can re-enter the production cycle for new battery manufacturing.
Can all EV batteries be recycled?
Most lithium-ion battery chemistries are recyclable. Technology continues improving to increase recovery efficiency across different cell designs.
What happens to an EV battery before it is recycled?
It is collected, discharged safely, dismantled, and sorted. Some are repurposed as secondary storage units before material recovery begins.
Is EV battery recycling environmentally friendly?
Recycling minimizes raw material extraction, reduces landfill waste, and lowers environmental risks. The sustainability outcome depends on recovery efficiency and facility practices.
Conclusion
EV battery recycling is becoming a structural component of modern electric mobility. As vehicle usage grows, the need for responsible end-of-life management increases. Recycling enables material recovery, promotes resource conservation, and aligns transportation systems with clean-energy objectives. Advancements in hydrometallurgical and closed-loop recovery offer promising pathways for future development, supported by policy, research, and industrial collaboration.
Understanding EV battery recycling today means recognizing how it affects resources, environment, and technological progress over the long term. Its evolution continues, influenced by innovation, policy direction, and sustainability priorities shaping global transportation.